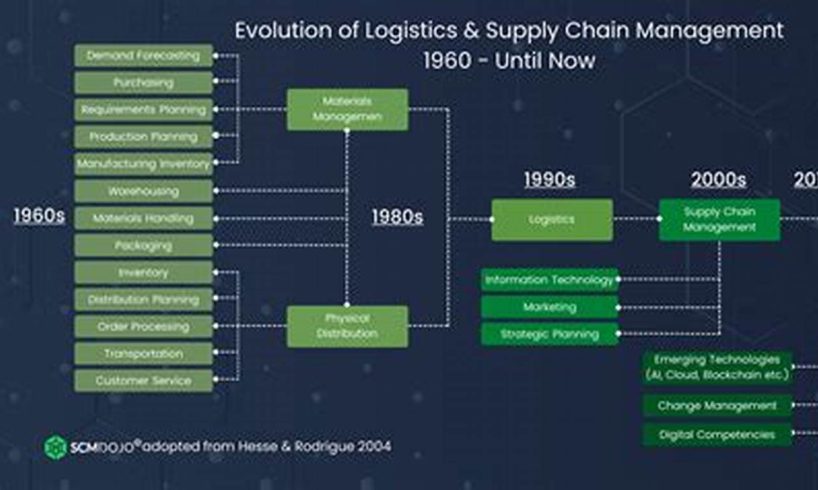
The 2000s logistics timeline encompasses a series of significant advancements that transformed the industry. It marked a period of rapid technological innovation, globalization, and supply chain optimization.
The rise of e-commerce during this time played a major role in shaping logistics trends. As online shopping gained popularity, businesses sought efficient and cost-effective ways to deliver products to consumers. This led to the adoption of advanced inventory management systems, automated warehouses, and real-time tracking technologies.
Moreover, globalization expanded markets and created new challenges for logistics providers. Companies faced the need to manage complex supply chains spanning different countries and continents. This required the development of global logistics networks, intermodal transportation systems, and customs clearance expertise.
The 2000s also witnessed a growing emphasis on sustainability in logistics. Businesses recognized the environmental impact of their operations and began to explore green logistics practices. This included the use of fuel-efficient vehicles, alternative energy sources, and waste reduction initiatives.
1. E-commerce boom
The e-commerce boom of the 2000s was a major catalyst for the transformation of the logistics industry. As online shopping gained popularity, businesses of all sizes needed to find efficient and cost-effective ways to deliver products to consumers.
This led to a surge in demand for logistics services, particularly in the areas of warehousing, transportation, and last-mile delivery. Logistics providers had to adapt quickly to meet the needs of e-commerce businesses, which often required faster delivery times, more flexible shipping options, and real-time tracking.
The e-commerce boom also accelerated the adoption of new technologies in the logistics industry. For example, many logistics providers began using warehouse management systems to improve inventory accuracy and order fulfillment. They also invested in automated warehouses to increase efficiency and reduce costs.
The connection between the e-commerce boom and the 2000’s logistics timeline is clear. The rapid growth of e-commerce created a need for new and innovative logistics solutions, which in turn led to the transformation of the industry.
2. Globalization
Globalization was a major force that shaped the 2000’s logistics timeline. As companies expanded their operations into new markets, they needed logistics providers who could manage complex supply chains spanning different countries and continents.
This led to the development of global logistics networks and intermodal transportation systems. Global logistics networks allowed companies to move goods from one country to another quickly and efficiently. Intermodal transportation systems allowed companies to use a combination of transportation modes, such as trucks, trains, and ships, to move goods around the world.
One of the most important aspects of globalization for the logistics industry was the growth of free trade agreements. Free trade agreements reduced or eliminated tariffs and other barriers to trade, making it easier for companies to move goods across borders.
The connection between globalization and the 2000’s logistics timeline is clear. Globalization created a need for new and innovative logistics solutions, which in turn led to the transformation of the industry.
3. Supply chain optimization
Supply chain optimization is the process of improving the efficiency and effectiveness of a supply chain. It involves coordinating all the activities involved in producing and delivering a product or service, from sourcing raw materials to delivering the finished product to the customer.
In the 2000s, supply chain optimization became increasingly important due to a number of factors, including globalization, the rise of e-commerce, and the increasing complexity of supply chains.
Globalization led to an increase in the number of suppliers and customers in different countries, making it more difficult to manage supply chains. The rise of e-commerce led to an increase in demand for fast and reliable delivery, which put pressure on supply chains to become more efficient.
To address these challenges, companies began to adopt new supply chain optimization technologies and practices. These included:
- Warehouse management systems
- Transportation management systems
- Inventory optimization software
- Vendor managed inventory
- Just-in-time manufacturing
These technologies and practices helped companies to improve their supply chain visibility, reduce inventory levels, and improve delivery times.
Supply chain optimization is a critical component of the 2000’s logistics timeline. It helped companies to meet the challenges of globalization, e-commerce, and supply chain complexity. It also laid the foundation for the continued evolution of the logistics industry in the 21st century.
4. Advanced inventory management
Advanced inventory management is the use of technology and best practices to optimize inventory levels and improve supply chain efficiency. It involves using data to track inventory levels, forecast demand, and make decisions about when and how to order new inventory.
In the 2000s, advanced inventory management became increasingly important due to a number of factors, including globalization, the rise of e-commerce, and the increasing complexity of supply chains.
Globalization led to an increase in the number of suppliers and customers in different countries, making it more difficult to manage inventory levels. The rise of e-commerce led to an increase in demand for fast and reliable delivery, which put pressure on companies to reduce inventory levels and improve delivery times.
To address these challenges, companies began to adopt new advanced inventory management technologies and practices. These included:
- Warehouse management systems
- Transportation management systems
- Inventory optimization software
- Vendor managed inventory
- Just-in-time manufacturing
These technologies and practices helped companies to improve their supply chain visibility, reduce inventory levels, and improve delivery times.
Advanced inventory management is a critical component of the 2000’s logistics timeline. It helped companies to meet the challenges of globalization, e-commerce, and supply chain complexity. It also laid the foundation for the continued evolution of the logistics industry in the 21st century.
5. Automated warehouses
Automated warehouses are a key component of the 2000’s logistics timeline. They are warehouses that use technology to automate tasks such as inventory management, order fulfillment, and shipping. Automated warehouses are becoming increasingly popular because they can help companies to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase productivity.
One of the biggest benefits of automated warehouses is that they can help companies to improve inventory accuracy. Automated warehouses use a variety of technologies, such as RFID tags and barcode scanners, to track inventory levels in real time. This information can be used to ensure that companies always have the right amount of inventory on hand, which can help to reduce costs and improve customer service.
Automated warehouses can also help companies to reduce labor costs. Automated warehouses use robots and other automated equipment to perform tasks that would otherwise be done by human workers. This can free up human workers to focus on more value-added activities, such as customer service and product development.
In addition to improving efficiency and reducing costs, automated warehouses can also help companies to increase productivity. Automated warehouses can operate 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, which can help companies to meet the demands of their customers. Automated warehouses can also help companies to improve order accuracy and reduce shipping times.
The use of automated warehouses is a key trend in the 2000’s logistics timeline. Automated warehouses are helping companies to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase productivity. As technology continues to develop, automated warehouses will become even more sophisticated and efficient.
6. Real-time tracking
Real-time tracking is the ability to track the location and status of assets, such as vehicles, inventory, and shipments, in real time. It is a key component of the 2000’s logistics timeline, as it has helped to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase visibility in the supply chain.
- Improved efficiency
Real-time tracking can help to improve efficiency by providing real-time visibility into the location and status of assets. This information can be used to optimize routing, reduce dwell times, and improve asset utilization.
- Reduced costs
Real-time tracking can help to reduce costs by reducing the need for manual tracking and by identifying inefficiencies in the supply chain. This information can be used to make informed decisions about how to improve operations and reduce costs.
- Increased visibility
Real-time tracking can help to increase visibility in the supply chain by providing real-time information about the location and status of assets. This information can be used to improve customer service, reduce risk, and make better decisions.
Real-time tracking is a key trend in the 2000’s logistics timeline. It is helping companies to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase visibility in the supply chain. As technology continues to develop, real-time tracking will become even more sophisticated and ubiquitous.
7. Global logistics networks
The development of global logistics networks was a key aspect of the 2000’s logistics timeline. These networks allowed companies to move goods from one country to another quickly and efficiently, which was essential for the growth of global trade.
- Improved efficiency
Global logistics networks helped to improve efficiency by reducing the time and cost of moving goods across borders. This was achieved through the use of standardized shipping containers, which made it easier to move goods between different modes of transport, such as ships, trains, and trucks.
- Reduced costs
Global logistics networks also helped to reduce costs by allowing companies to take advantage of economies of scale. By shipping goods in bulk, companies could reduce the cost per unit of shipping.
- Increased flexibility
Global logistics networks also increased flexibility by allowing companies to respond quickly to changes in demand. For example, if there was a sudden increase in demand for a particular product in one country, companies could quickly ship goods from another country to meet that demand.
- Improved customer service
Global logistics networks also improved customer service by allowing companies to deliver goods to customers quickly and reliably. This was essential for the growth of e-commerce, which requires companies to be able to deliver goods to customers anywhere in the world.
The development of global logistics networks was a major factor in the growth of global trade in the 2000s. These networks allowed companies to move goods from one country to another quickly, efficiently, and cost-effectively. This helped to reduce the cost of goods for consumers and businesses, and it also made it easier for companies to compete in the global marketplace.
8. Intermodal transportation
Intermodal transportation, a cornerstone of the 2000’s logistics timeline, emerged as a game-changer in the seamless movement of goods across diverse geographies. It involves utilizing multiple modes of transportation, such as trucks, trains, ships, and airplanes, to deliver shipments to their final destinations. This interconnected approach revolutionized supply chains, offering numerous advantages that reshaped the logistics landscape during this transformative era.
- Cost-effectiveness
Intermodal transportation optimizes costs by leveraging the strengths of each mode of transport. For instance, railroads provide cost-efficient long-distance hauling, while trucks enable flexible door-to-door delivery. By combining these modes, businesses can achieve a balance between cost and efficiency.
- Environmental sustainability
Intermodal transportation promotes environmental sustainability. Railroads and ships emit significantly lower carbon emissions compared to trucks, reducing the overall carbon footprint of supply chains. This aligns with the growing emphasis on eco-friendly practices within the logistics industry.
- Reliability and efficiency
Intermodal transportation enhances reliability and efficiency by minimizing touchpoints and optimizing transit times. The seamless transfer of goods between different modes reduces handling and potential delays, ensuring timely delivery to customers.
- Flexibility and adaptability
Intermodal transportation offers flexibility and adaptability to meet diverse shipping needs. It allows businesses to tailor their transportation strategies based on factors such as shipment size, time constraints, and cost considerations. This versatility empowers businesses to respond effectively to market demands and supply chain disruptions.
In summary, intermodal transportation played a pivotal role in the 2000’s logistics timeline, transforming supply chains through its cost-effectiveness, environmental sustainability, reliability, and adaptability. As the logistics industry continues to evolve, intermodal transportation remains a cornerstone, enabling businesses to optimize their operations and deliver goods to customers efficiently and sustainably.
9. Sustainability
The concept of sustainability emerged as a driving force within the logistics industry during the 2000’s logistics timeline. Companies recognized the pressing need to minimize their environmental impact and operate in a socially responsible manner. Sustainability became a key consideration in logistics decision-making, leading to the adoption of innovative practices and technologies.
- Environmental stewardship
Logistics companies implemented measures to reduce their carbon footprint, conserve natural resources, and minimize waste. This included using fuel-efficient vehicles, optimizing routes to reduce miles, and implementing recycling and waste reduction programs.
- Social responsibility
Sustainability extended beyond environmental concerns to encompass social responsibility. Logistics companies focused on improving the working conditions of their employees, ensuring fair labor practices, and supporting local communities through charitable initiatives.
- Ethical sourcing
Companies became more mindful of the ethical implications of their sourcing practices. They sought to ensure that the materials and products they used were sourced from suppliers who adhered to ethical and sustainable standards.
- Sustainable packaging
Logistics companies began to explore sustainable packaging solutions to reduce waste and minimize the environmental impact of packaging materials. This included using biodegradable and recyclable materials, as well as implementing packaging optimization techniques.
The integration of sustainability into the 2000’s logistics timeline had a profound impact on the industry. It drove innovation, raised awareness of environmental and social issues, and set a new standard for responsible business practices. Sustainability remains a cornerstone of logistics operations today, as companies continue to seek ways to minimize their environmental footprint and operate in a sustainable and ethical manner.
FAQs on “2000’s Logistics Timeline”
This section addresses frequently asked questions related to the “2000’s Logistics Timeline” to clarify common misconceptions and provide comprehensive insights.
Question 1: What were the key factors that drove the transformation of the logistics industry in the 2000s?
The 2000’s logistics timeline was shaped by several key factors, including the e-commerce boom, globalization, supply chain optimization, advanced inventory management, automated warehouses, real-time tracking, global logistics networks, intermodal transportation, and sustainability.
Question 2: How did e-commerce contribute to the evolution of logistics in the 2000s?
The e-commerce boom created a surge in demand for efficient and cost-effective logistics solutions. It accelerated the adoption of advanced inventory management systems, automated warehouses, and real-time tracking technologies to meet the needs of online businesses.
Question 3: What was the significance of globalization in the 2000’s logistics timeline?
Globalization led to the expansion of markets and created challenges for logistics providers in managing complex supply chains across different countries. It necessitated the development of global logistics networks, intermodal transportation systems, and customs clearance expertise.
Question 4: How did sustainability become an integral part of logistics operations in the 2000s?
Recognizing the environmental impact of their operations, businesses embraced sustainability practices in the 2000s. This included using eco-friendly vehicles, optimizing routes to reduce emissions, and implementing recycling and waste reduction programs.
Question 5: What were the benefits of adopting intermodal transportation in the 2000’s logistics timeline?
Intermodal transportation offered numerous advantages, such as cost-effectiveness, environmental sustainability, reliability, and flexibility. It enabled businesses to optimize costs and reduce carbon emissions while improving transit times and adapting to diverse shipping needs.
Question 6: How did technological advancements contribute to the transformation of logistics in the 2000s?
Technological advancements played a crucial role in streamlining logistics operations. Advanced inventory management systems, warehouse management systems, and real-time tracking technologies enhanced inventory accuracy, order fulfillment, and supply chain visibility.
In summary, the “2000’s Logistics Timeline” marked a period of significant transformation driven by various factors, including technological advancements, globalization, sustainability concerns, and the rise of e-commerce. These factors collectively reshaped the industry, laying the foundation for continued evolution in the years to come.
Transition to the next article section…
Tips to Optimize Logistics Operations
Harnessing insights from the “2000’s Logistics Timeline,” businesses can adopt effective strategies to enhance their logistics operations in the modern era.
Tip 1: Embrace Technological Advancements
Implement advanced inventory management systems, warehouse management systems, and real-time tracking technologies to improve inventory accuracy, order fulfillment, and supply chain visibility.
Tip 2: Optimize Supply Chain Networks
Analyze and optimize supply chain networks to reduce lead times, minimize inventory levels, and enhance overall efficiency.
Tip 3: Leverage Intermodal Transportation
Utilize intermodal transportation to optimize costs, reduce carbon emissions, improve reliability, and enhance flexibility in shipping operations.
Tip 4: Focus on Sustainability
Incorporate sustainable practices into logistics operations, such as using eco-friendly vehicles, implementing recycling programs, and minimizing waste.
Tip 5: Cultivate Strategic Partnerships
Establish strong partnerships with logistics providers, technology vendors, and other stakeholders to leverage expertise and drive innovation.
Tip 6: Invest in Employee Development
Provide training and development opportunities for logistics professionals to enhance their skills and adapt to the evolving industry landscape.
Tip 7: Monitor Industry Trends
Stay abreast of emerging technologies, best practices, and industry trends to identify opportunities for continuous improvement.
Tip 8: Measure and Analyze Performance
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and regularly measure and analyze logistics performance to identify areas for improvement and optimization.
By implementing these tips, businesses can harness the lessons from the “2000’s Logistics Timeline” and optimize their logistics operations for improved efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability.
Transition to the conclusion of the article…
Conclusion
The “2000’s Logistics Timeline” serves as a testament to the transformative power of innovation and globalization in shaping the logistics industry. Technological advancements, the rise of e-commerce, and the emphasis on sustainability have propelled the industry towards greater efficiency, connectivity, and environmental consciousness.
As we move forward, it is imperative for businesses to embrace these lessons and continue investing in innovation. By leveraging advanced technologies, optimizing supply chains, adopting sustainable practices, and fostering strategic partnerships, organizations can position themselves for success in the ever-evolving logistics landscape.
The “2000’s Logistics Timeline” not only documents the past but also provides a roadmap for the future. By harnessing the insights gained from this era, businesses can drive operational excellence, reduce costs, enhance customer satisfaction, and contribute to a more sustainable and efficient global supply chain.






