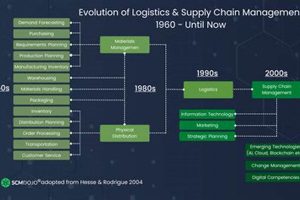
In the 2000s, the advent of cloud computing revolutionized logistics and supply chain management, offering a suite of technologies and services that transformed the industry.
Cloud computing enabled logistics companies to access and leverage computing resources, storage, and applications over the internet, eliminating the need for costly on-premises infrastructure and software. This paradigm shift brought about numerous benefits, including improved efficiency, reduced costs, enhanced collaboration, and real-time visibility into supply chains.
As a result, logistics providers could streamline their operations, automate tasks, and gain a comprehensive understanding of their supply chains. Cloud-based solutions facilitated real-time tracking of shipments, inventory management, demand forecasting, and data analytics, empowering logistics companies to make informed decisions and optimize their operations.
1. Scalability
Scalability was a key factor in the transformative impact of cloud computing on 2000s logistics. Before cloud computing, logistics companies were constrained by the capacity of their on-premises infrastructure. To handle increased demand, they had to invest in additional hardware and software, which could be a costly and time-consuming process.
Cloud computing eliminated this constraint. By leveraging cloud-based platforms, logistics companies could access virtually unlimited computing resources on a pay-as-you-go basis. This allowed them to scale their operations up or down as needed, without the need for upfront investment or long-term commitments.
For example, a logistics company experiencing a surge in demand during the holiday season could easily scale up its operations by provisioning additional cloud resources. Once the peak season passed, the company could scale back its operations and reduce its cloud spend.
This scalability was essential for logistics companies to meet the evolving demands of the global supply chain. It enabled them to handle fluctuations in demand, optimize their resource utilization, and reduce their overall costs.
2. Cost-effectiveness
In the early 2000s, logistics companies heavily relied on on-premises infrastructure to manage their operations. However, this approach was often costly and inefficient. On-premises infrastructure required significant capital expenditure, ongoing maintenance, and upgrades to keep pace with evolving technology.
- Reduced capital expenditure
Cloud computing eliminated the need for logistics companies to invest in expensive hardware and software. Instead, they could access computing resources and applications over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis.
- Lower ongoing maintenance costs
With cloud computing, logistics companies no longer had to worry about the maintenance and upkeep of their on-premises infrastructure. This responsibility shifted to the cloud provider, reducing the burden on logistics companies’ IT teams and freeing up resources for other initiatives.
- Increased flexibility and scalability
Cloud computing provided logistics companies with the flexibility to scale their operations up or down as needed, without the need for additional capital investment. This flexibility was essential for meeting fluctuating demand and optimizing resource utilization.
- Improved cost predictability
Cloud computing introduced a more predictable cost structure for logistics companies. Instead of large upfront investments, companies could budget for their cloud usage on a monthly or annual basis.
Overall, the cost-effectiveness of cloud computing was a major factor in its adoption by logistics companies in the 2000s. It enabled them to reduce their capital expenditure, lower their ongoing maintenance costs, and gain greater flexibility and scalability.
3. Flexibility
Flexibility was a crucial component of what cloud computing did for 2000s logistics. Before cloud computing, logistics companies were constrained by the inflexibility of their on-premises infrastructure. Scaling operations up or down was a time-consuming and costly process, making it difficult to adapt to changing market demands and customer requirements.
Cloud computing eliminated this inflexibility. By leveraging cloud-based solutions, logistics companies gained the ability to scale their operations up or down quickly and easily. This flexibility was essential for meeting the evolving demands of the global supply chain. For example, a logistics company could easily increase its capacity to handle a surge in demand during the holiday season and then scale back down once the peak season passed.
In addition to scaling, cloud-based solutions also provided logistics companies with the flexibility to adapt to changing customer requirements. For example, a logistics company could quickly add new features or services to its offerings without having to invest in new hardware or software. This flexibility was essential for logistics companies to remain competitive and meet the needs of their customers.
Overall, the flexibility provided by cloud-based solutions was a major factor in the transformative impact of cloud computing on 2000s logistics. It enabled logistics companies to adapt to changing market demands and customer requirements, improve their agility, and gain a competitive advantage.
4. Collaboration
Collaboration is a key aspect of what cloud computing did for 2000s logistics. Before cloud computing, logistics companies were often constrained by disparate systems and processes, making it difficult to collaborate effectively with other stakeholders in the supply chain. This lack of collaboration led to inefficiencies, delays, and errors.
- Real-time visibility
Cloud computing provided logistics companies with real-time visibility into their supply chains. This visibility enabled different stakeholders to track the progress of shipments, inventory levels, and other key metrics in real time. This improved communication and coordination among stakeholders, as they could all access the same up-to-date information.
- Centralized communication
Cloud-based platforms provided a central communication hub for different stakeholders in the supply chain. This enabled them to communicate and share information more easily, reducing the risk of miscommunication and errors. For example, logistics companies could use cloud-based platforms to share shipping updates, inventory levels, and other relevant information with their customers and suppliers.
- Automated workflows
Cloud computing enabled the automation of many tasks in the supply chain, such as order processing, inventory management, and shipment tracking. This automation freed up logistics professionals to focus on higher-value activities, such as building relationships with customers and suppliers. Automated workflows also improved the accuracy and efficiency of supply chain operations.
- Improved decision-making
Cloud computing provided logistics companies with access to powerful data analytics tools. These tools enabled them to analyze vast amounts of data to identify trends, optimize operations, and make better decisions. For example, logistics companies could use data analytics to identify inefficiencies in their supply chains and develop strategies to improve them.
Overall, cloud computing’s facilitation of seamless collaboration among different stakeholders in the supply chain was a major factor in its transformative impact on 2000s logistics. It improved communication and coordination, automated tasks, and provided logistics companies with the insights they needed to make better decisions.
5. Real-time visibility
Real-time visibility was a game-changer for logistics companies in the 2000s. Before cloud computing, logistics companies were often flying blind, relying on manual processes and outdated information to manage their supply chains. This lack of visibility led to inefficiencies, delays, and errors.
Cloud-based platforms changed all that. By providing real-time visibility into supply chain operations, cloud computing enabled logistics companies to track shipments, manage inventory, and respond to disruptions in real time. This led to a number of benefits, including:
- Improved efficiency: With real-time visibility, logistics companies could identify and bottlenecks in their supply chains. This led to faster delivery times and reduced costs.
- Reduced inventory levels: With real-time visibility into inventory levels, logistics companies could reduce their inventory levels without sacrificing customer service. This led to reduced carrying costs and improved cash flow.
- Improved customer service: With real-time visibility into the status of shipments, logistics companies could provide better customer service. Customers could track their shipments online and receive updates on delivery times.
Here is an example of how real-time visibility helped a logistics company in the 2000s:
A large retail company was experiencing problems with its supply chain. The company was often out of stock of popular items, and customers were complaining about late deliveries. The company implemented a cloud-based supply chain management system that provided real-time visibility into its operations. The system helped the company to identify and bottlenecks in its supply chain. The company also used the system to improve its inventory management and customer service. As a result, the company was able to reduce its out-of-stock rates, improve delivery times, and increase customer satisfaction.
Real-time visibility was a key component of what cloud computing did for 2000s logistics. It enabled logistics companies to improve their efficiency, reduce their costs, and improve their customer service.
6. Automation
The automation of repetitive tasks was a significant aspect of cloud computing’s transformative impact on 2000s logistics. Prior to cloud computing, logistics companies heavily relied on manual processes for tasks such as order processing, inventory management, and shipment tracking. These tasks were time-consuming and error-prone, diverting valuable human resources away from higher-value activities that could drive business growth.
- Increased efficiency and productivity
Cloud-based automation solutions streamlined these repetitive tasks, reducing the time and effort required to complete them. This freed up logistics professionals to focus on more strategic activities, such as developing new business opportunities, improving customer service, and optimizing supply chain operations.
- Enhanced accuracy and reliability
Automated systems are less prone to errors compared to manual processes. By eliminating human error, cloud computing improved the accuracy and reliability of logistics operations, reducing the risk of lost or delayed shipments, incorrect inventory counts, and other costly mistakes.
- Reduced labor costs
The automation of repetitive tasks also led to reduced labor costs for logistics companies. By eliminating the need for manual labor, companies could reduce their workforce or redeploy employees to more value-added roles, optimizing their overall cost structure.
- Improved scalability
Cloud-based automation solutions are highly scalable, allowing logistics companies to easily adjust their automation capabilities to meet changing business demands. This scalability was particularly valuable during peak seasons or periods of rapid growth, ensuring that logistics operations could continue to function efficiently without disruption.
In summary, the automation of repetitive tasks through cloud computing in the 2000s logistics industry revolutionized the way logistics companies operated. It increased efficiency, enhanced accuracy, reduced costs, improved scalability, and allowed logistics professionals to focus on higher-value activities that drove business growth and customer satisfaction.
7. Data analytics
In the context of “what did cloud computing do in the 2000s logistics,” data analytics played a transformative role. Cloud computing empowered logistics companies with sophisticated tools to analyze vast amounts of data in a cost-effective and scalable manner, leading to significant improvements in logistics operations and decision-making.
- Real-time visibility and predictive analytics
Cloud-based data analytics enabled logistics companies to gain real-time visibility into their supply chains, including inventory levels, shipment locations, and order fulfillment status. This visibility facilitated predictive analytics, allowing companies to forecast demand, identify potential disruptions, and optimize inventory allocation based on data-driven insights.
- Customer behavior analysis
Data analytics provided logistics companies with a deeper understanding of customer behavior and preferences. By analyzing data on purchase history, delivery preferences, and customer feedback, logistics companies could personalize their services, improve delivery routes, and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
- Operational efficiency and cost optimization
Data analytics helped logistics companies identify inefficiencies and optimize their operations. By analyzing data on resource utilization, delivery times, and fuel consumption, companies could identify areas for improvement, reduce operational costs, and increase overall productivity.
- Decision support and strategic planning
Data analytics provided logistics companies with valuable insights to support decision-making and strategic planning. By analyzing data on market trends, competitor performance, and industry best practices, companies could make informed decisions about investments, partnerships, and long-term growth strategies.
In summary, data analytics, enabled by cloud computing, transformed logistics operations and decision-making in the 2000s. It provided logistics companies with real-time visibility, predictive capabilities, customer insights, operational efficiency, and strategic planning support, enabling them to navigate the complexities of the global supply chain and gain a competitive advantage.
FAQs about “What Did Cloud Computing Do in the 2000s Logistics?”
This section addresses frequently asked questions regarding the impact of cloud computing on the logistics industry in the 2000s, providing concise and informative answers.
Question 1: How did cloud computing improve efficiency in logistics?
Cloud computing enabled logistics companies to automate repetitive tasks, streamline processes, and gain real-time visibility into their supply chains. This led to reduced operational costs, improved inventory management, and faster delivery times.
Question 2: What were the cost benefits of cloud computing for logistics companies?
Cloud computing eliminated the need for expensive on-premises infrastructure, reduced maintenance costs, and provided flexible pricing models. This allowed logistics companies to scale their operations cost-effectively and avoid large upfront investments.
Question 3: How did cloud computing enhance collaboration in the supply chain?
Cloud-based platforms facilitated seamless communication and data sharing among different stakeholders in the supply chain. This improved coordination, reduced errors, and enabled real-time decision-making.
Question 4: What role did data analytics play in cloud-based logistics?
Data analytics tools provided logistics companies with valuable insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operational performance. This enabled data-driven decision-making, predictive analytics, and optimization of logistics operations.
Question 5: How did cloud computing impact the scalability of logistics operations?
Cloud computing offered scalable solutions that allowed logistics companies to adjust their operations based on demand fluctuations. This flexibility enabled them to meet peak season demands, handle unexpected disruptions, and optimize resource utilization.
Question 6: What were the overall benefits of cloud computing for the logistics industry?
In summary, cloud computing transformed the logistics industry in the 2000s by enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, improving collaboration, enabling data-driven decision-making, providing scalability, and driving overall innovation.
This comprehensive overview of frequently asked questions provides a deeper understanding of the impact and benefits of cloud computing in revolutionizing the logistics industry during the early 2000s.
Transition to the next article section: The evolution of cloud computing in logistics continues to shape the industry, with ongoing advancements and new opportunities. The next section of this article will delve into the latest trends and innovations in cloud-based logistics.
Tips to Enhance Logistics with Cloud Computing
To effectively leverage cloud computing for logistics improvements, consider these valuable tips:
Tip 1: Prioritize Scalability and Flexibility:
Choose cloud solutions that offer scalability to adapt to fluctuating demand and seasonal variations. This flexibility ensures your logistics operations can seamlessly handle peaks and troughs, optimizing resource utilization and reducing costs.
Tip 2: Embrace Real-Time Visibility:
Implement cloud-based platforms that provide real-time visibility into your supply chain. This enables proactive monitoring of shipments, inventory levels, and potential disruptions, allowing for swift decision-making and efficient issue resolution.
Tip 3: Leverage Data Analytics for Optimization:
Utilize cloud computing’s data analytics capabilities to analyze vast amounts of logistics data. Identify trends, optimize routes, and make data-driven decisions to improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Tip 4: Enhance Collaboration through Cloud Platforms:
Facilitate seamless collaboration among different stakeholders in the supply chain by adopting cloud-based platforms. This improves communication, streamlines data sharing, and fosters better coordination, reducing errors and improving overall supply chain performance.
Tip 5: Automate Repetitive Tasks:
Leverage cloud computing to automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks such as order processing, inventory management, and shipment tracking. This frees up your logistics team to focus on more strategic and value-added activities that drive growth and innovation.
Tip 6: Consider Cost Optimization Strategies:
Explore cloud pricing models and negotiate cost-effective contracts to optimize your cloud computing investment. Utilize cloud features like pay-as-you-go and spot instances to minimize expenses and maximize ROI.
By implementing these tips, logistics companies can harness the full potential of cloud computing to transform their operations, gain a competitive edge, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
Conclusion: Cloud computing has revolutionized logistics, providing a suite of technologies and services that have transformed the industry. By embracing cloud solutions, logistics companies can achieve greater efficiency, cost optimization, flexibility, and data-driven decision-making.
Conclusion
In the early 2000s, the advent of cloud computing revolutionized the logistics industry, bringing about a paradigm shift in how logistics companies operated and managed their supply chains. Cloud-based solutions offered scalability, cost-effectiveness, flexibility, real-time visibility, data analytics, and automation, empowering logistics companies to transform their operations and gain a competitive advantage.
This comprehensive exploration of “what did cloud computing do in the 2000s logistics” has shed light on the profound impact of cloud computing on the industry. Cloud computing enabled logistics companies to streamline their processes, reduce costs, improve collaboration, optimize decision-making, and adapt to evolving market demands. The adoption of cloud solutions transformed the logistics landscape, setting the stage for continued innovation and growth in the years to come.