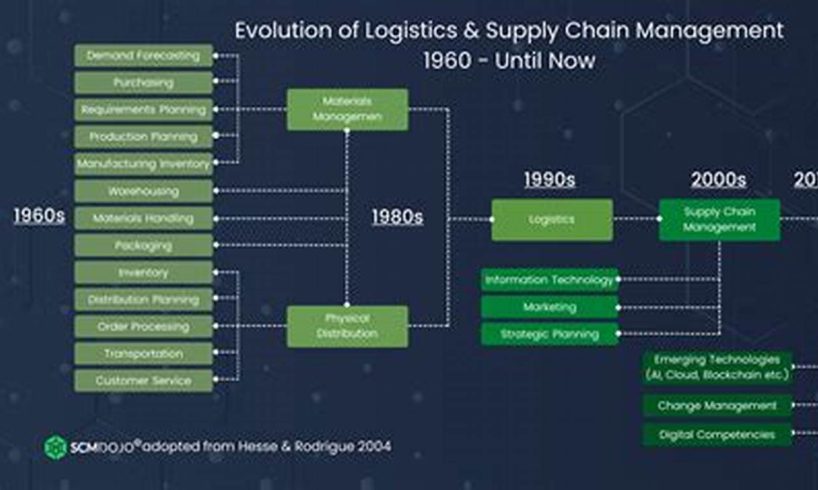
Technology in Logistics Timeline refers to the historical evolution and advancements in the use of technology within the logistics industry. It encompasses the various technological innovations and their impact on logistics operations, from the early days of manual processes to the present era of digitalization and automation.
The integration of technology in logistics has revolutionized the way goods and materials are transported, stored, and managed. It has brought about significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, visibility, and cost-effectiveness. Moreover, technology has played a crucial role in enhancing customer service, optimizing inventory levels, and reducing waste.
The timeline of technology in logistics is marked by several key milestones, including the introduction of computers in the 1960s, the development of barcode technology in the 1970s, the emergence of electronic data interchange (EDI) in the 1980s, the widespread adoption of the internet in the 1990s, and the rise of cloud computing, big data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) in recent years.
As we move forward, technology is expected to continue to shape the logistics industry, with emerging technologies such as blockchain, robotics, and autonomous vehicles poised to further transform logistics operations and supply chains.
1. Automation
Automation is a key aspect of technology in logistics timeline, playing a pivotal role in revolutionizing logistics operations. It involves the use of technology to perform tasks that were previously done manually, leading to increased efficiency, reduced labor costs, and improved accuracy.
One of the earliest examples of automation in logistics was the introduction of automated guided vehicles (AGVs) in the 1950s. AGVs are driverless vehicles that can transport goods within warehouses and distribution centers, following predetermined paths. Since then, automation has become increasingly sophisticated, with the advent of robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning.
Today, automation is used in various areas of logistics, including:
- Material handling: Automated systems can load, unload, and transport goods within warehouses and distribution centers.
- Order fulfillment: Automated systems can pick, pack, and sort orders, reducing the need for manual labor.
- Transportation: Self-driving trucks and drones are being developed to automate the transportation of goods over long distances.
The practical significance of automation in logistics is immense. It can lead to significant cost savings, improved productivity, and reduced errors. Moreover, automation can free up human workers to focus on more complex and value-added tasks.
2. Efficiency
Efficiency is a crucial aspect of technology in logistics timeline, underpinning the drive to optimize logistics operations and deliver goods and services in a timely, cost-effective manner. Technology has played a transformative role in improving efficiency across the logistics industry, from streamlining processes to enhancing visibility and control.
One of the key ways in which technology has improved efficiency in logistics is through automation. Automated systems, such as automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and robotic picking systems, can perform repetitive tasks with greater speed and accuracy than manual labor. This not only reduces labor costs but also frees up human workers to focus on more complex and value-added tasks.
Another way in which technology has improved efficiency in logistics is through the use of data analytics. By collecting and analyzing data from various sources, logistics providers can gain valuable insights into their operations. This data can be used to identify inefficiencies, optimize routes, and make better decisions about inventory management.
The practical significance of efficiency in logistics is immense. Improved efficiency can lead to significant cost savings, reduced lead times, and improved customer satisfaction. In today’s competitive business environment, logistics providers that can operate efficiently have a clear advantage over their competitors.
3. Visibility
In the context of technology in logistics timeline, visibility refers to the ability to track and monitor the movement of goods and materials throughout the supply chain. It provides real-time information about the location, status, and condition of shipments, enabling logistics providers to make informed decisions and respond quickly to disruptions.
- Real-time tracking: GPS tracking devices and RFID tags allow logistics providers to track the location of shipments in real time. This information can be accessed through online dashboards or mobile apps, providing up-to-date visibility of the entire supply chain.
- Shipment status updates: Technology enables logistics providers to provide regular updates on the status of shipments, including estimated arrival times, delays, and any issues that may arise. This information can be shared with customers to keep them informed and manage expectations.
- Condition monitoring: Sensors and IoT devices can be used to monitor the condition of goods in transit, such as temperature, humidity, and shock. This information can be used to ensure that goods are transported in optimal conditions and to identify any potential issues before they cause damage or spoilage.
- End-to-end visibility: Technology can provide end-to-end visibility across the entire supply chain, from the point of origin to the final destination. This allows logistics providers to identify inefficiencies, optimize routes, and collaborate with partners to improve overall performance.
The practical significance of visibility in logistics is immense. Improved visibility can lead to reduced lead times, increased inventory accuracy, better customer service, and reduced costs. In today’s competitive business environment, logistics providers that can provide real-time visibility have a clear advantage over their competitors.
4. Cost-effectiveness
Cost-effectiveness is a critical aspect of technology in logistics timeline, driven by the need to optimize logistics operations and reduce costs while maintaining or improving service levels. Technology has played a pivotal role in enhancing cost-effectiveness across the logistics industry, from reducing labor costs to optimizing inventory management and transportation routes.
One of the key ways in which technology has improved cost-effectiveness in logistics is through automation. Automated systems, such as automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and robotic picking systems, can perform repetitive tasks with greater speed and accuracy than manual labor. This not only reduces labor costs but also frees up human workers to focus on more complex and value-added tasks.
Another way in which technology has improved cost-effectiveness in logistics is through the use of data analytics. By collecting and analyzing data from various sources, logistics providers can gain valuable insights into their operations. This data can be used to identify inefficiencies, optimize routes, and make better decisions about inventory management. By leveraging data analytics, logistics providers can reduce waste, lower transportation costs, and improve overall operational efficiency.
The practical significance of cost-effectiveness in logistics is immense. Improved cost-effectiveness can lead to significant cost savings, which can be passed on to customers in the form of lower prices or invested in other areas of the business. In today’s competitive business environment, logistics providers that can operate cost-effectively have a clear advantage over their competitors.
5. Customer service
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology in logistics timeline, customer service has emerged as a critical differentiator for logistics providers. Technology has played a transformative role in enhancing customer service, enabling logistics providers to offer real-time visibility, personalized experiences, and proactive support.
- Real-time visibility: Technology has empowered logistics providers to offer real-time visibility into the location and status of shipments. Customers can track their shipments online or through mobile apps, receiving up-to-date information on estimated arrival times, delays, and any issues that may arise. This transparency fosters trust and reduces customer anxiety.
- Personalized experiences: Technology enables logistics providers to tailor their services to meet the specific needs of each customer. By leveraging data analytics, logistics providers can gain insights into customer preferences and behaviors, allowing them to offer customized shipping options, proactive notifications, and personalized communication.
- Proactive support: Technology has made it possible for logistics providers to offer proactive support to their customers. Predictive analytics and AI-powered chatbots can identify potential issues before they occur and proactively notify customers, enabling them to take timely action and mitigate disruptions.
- Omnichannel support: Technology has facilitated the integration of multiple communication channels, allowing customers to reach logistics providers through phone, email, chat, social media, and self-service portals. This omnichannel approach provides customers with flexibility and convenience, enhancing the overall customer experience.
By embracing technology and investing in customer service, logistics providers can differentiate themselves in the market, build stronger customer relationships, and drive customer loyalty. In the technology in logistics timeline, customer service has become a key pillar for logistics providers seeking to succeed in the digital age.
6. Inventory optimization
Inventory optimization is a crucial aspect of technology in logistics timeline, driven by the need to minimize inventory holding costs while maintaining desired service levels. Technology has played a transformative role in inventory optimization, enabling logistics providers to leverage data and analytics to make informed decisions about inventory management.
One of the key ways in which technology has improved inventory optimization is through the use of data analytics. By collecting and analyzing data from various sources, such as sales history, demand forecasting, and supplier lead times, logistics providers can gain valuable insights into their inventory patterns. This data can be used to identify slow-moving items, optimize safety stock levels, and make better decisions about when and how much to order.
Another way in which technology has improved inventory optimization is through the use of inventory management software. This software can help logistics providers track inventory levels in real time, manage multiple warehouses, and automate inventory replenishment. By leveraging inventory management software, logistics providers can reduce the risk of stockouts, improve inventory accuracy, and free up human workers to focus on more strategic tasks.
The practical significance of inventory optimization in the technology in logistics timeline is immense. Optimized inventory levels can lead to significant cost savings, improved customer service, and increased profitability. In today’s competitive business environment, logistics providers that can optimize their inventory effectively have a clear advantage over their competitors.
7. Data analytics
Data analytics has played a transformative role in the evolution of technology in logistics timeline. By leveraging data and analytics, logistics providers have gained valuable insights into their operations, enabling them to improve efficiency, optimize inventory, and enhance customer service.
- Predictive analytics: Predictive analytics uses historical data and machine learning algorithms to forecast future demand and trends. This information can be used to optimize inventory levels, plan transportation routes, and make better decisions about pricing and promotions.
- Prescriptive analytics: Prescriptive analytics goes beyond predictive analytics by providing specific recommendations on what actions to take. This information can be used to optimize warehouse operations, improve customer service, and reduce costs.
- Real-time analytics: Real-time analytics involves the analysis of data as it is generated. This information can be used to monitor the performance of logistics operations, identify potential problems, and take corrective action in real time.
- Big data analytics: Big data analytics involves the analysis of large and complex data sets. This information can be used to identify patterns and trends that would be difficult to find using traditional data analysis techniques.
The practical significance of data analytics in technology in logistics timeline is immense. Data analytics can lead to significant cost savings, improved customer service, and increased profitability. In today’s competitive business environment, logistics providers that can effectively leverage data analytics have a clear advantage over their competitors.
8. Sustainability
Sustainability has become an increasingly important consideration in the technology in logistics timeline, as businesses strive to reduce their environmental impact and operate in a more sustainable manner.
- Green transportation: The use of technology to reduce emissions and improve fuel efficiency in transportation operations, such as electric vehicles, hybrid vehicles, and route optimization software.
- Renewable energy: The use of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to power logistics operations, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Sustainable packaging: The use of sustainable packaging materials, such as biodegradable and recyclable materials, to reduce waste and environmental impact.
- Reverse logistics: The use of technology to improve the efficiency of reverse logistics operations, such as product returns and end-of-life management, reducing waste and environmental impact.
By embracing sustainability, logistics providers can not only reduce their environmental impact but also improve their efficiency and profitability. In today’s competitive business environment, logistics providers that can operate sustainably have a clear advantage over their competitors.
Frequently Asked Questions about Technology in Logistics Timeline
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions about the technology in logistics timeline, providing concise and informative answers.
Question 1: What are the key milestones in the technology in logistics timeline?
Answer: Key milestones include the introduction of computers in the 1960s, the development of barcode technology in the 1970s, the emergence of electronic data interchange (EDI) in the 1980s, the widespread adoption of the internet in the 1990s, and the rise of cloud computing, big data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) in recent years.
Question 2: How has technology improved efficiency in logistics?
Answer: Technology has improved efficiency through automation, data analytics, and improved visibility. Automation has led to increased speed and accuracy, while data analytics has enabled logistics providers to optimize routes and make better decisions about inventory management. Improved visibility has reduced lead times and increased inventory accuracy.
Question 3: How has technology enhanced customer service in logistics?
Answer: Technology has enhanced customer service through real-time visibility, personalized experiences, and proactive support. Real-time visibility allows customers to track their shipments, while personalized experiences and proactive support ensure that customers receive tailored services and timely assistance.
Question 4: What are the benefits of inventory optimization in logistics?
Answer: Inventory optimization reduces inventory holding costs while maintaining desired service levels. It leads to significant cost savings, improved customer service, and increased profitability.
Question 5: How does data analytics contribute to the technology in logistics timeline?
Answer: Data analytics provides valuable insights into logistics operations, enabling logistics providers to improve efficiency, optimize inventory, and enhance customer service. Predictive analytics, prescriptive analytics, real-time analytics, and big data analytics are key types of data analytics used in logistics.
Question 6: How is sustainability incorporated into the technology in logistics timeline?
Answer: Sustainability is incorporated into the technology in logistics timeline through green transportation, renewable energy, sustainable packaging, and reverse logistics. These practices reduce environmental impact and improve efficiency and profitability.
Summary: Technology has revolutionized the logistics industry, improving efficiency, visibility, cost-effectiveness, customer service, inventory optimization, and sustainability. By embracing technology, logistics providers can gain a competitive advantage and meet the evolving demands of the modern supply chain.
Transition to the next article section: Explore the latest advancements and emerging trends in the technology in logistics timeline, shaping the future of logistics operations.
Tips for Embracing Technology in Logistics
To successfully embrace technology in logistics, consider these practical tips:
Tip 1: Assess your current technology landscape.
Evaluate your existing technology infrastructure, processes, and capabilities. Identify areas for improvement and opportunities to integrate new technologies.
Tip 2: Define your technology goals.
Determine the specific outcomes you aim to achieve with technology adoption. Align your technology goals with your overall business objectives.
Tip 3: Research and select the right technologies.
Explore different technologies available in the market. Consider their features, benefits, and compatibility with your existing systems.
Tip 4: Implement technology in phases.
Break down your technology implementation into smaller, manageable phases. This allows for better planning, testing, and risk management.
Tip 5: Train your team on new technologies.
Provide comprehensive training to your team to ensure they are proficient in using new technologies and processes. This fosters adoption and maximizes the benefits.
Tip 6: Monitor and evaluate your technology investments.
Regularly track the performance of your technology investments. Measure key metrics and make adjustments as needed to optimize results.
By following these tips, you can effectively embrace technology in logistics and drive innovation, efficiency, and customer satisfaction within your organization.
Summary: Technology adoption in logistics is crucial for businesses seeking to stay competitive and meet evolving customer demands. A well-planned and executed technology strategy can transform logistics operations, leading to significant improvements in efficiency, visibility, cost-effectiveness, and customer service.
Technology in Logistics Timeline
The evolution of technology in logistics has transformed the industry, driving efficiency, visibility, cost-effectiveness, customer service, inventory optimization, and sustainability. From the early days of manual processes to the present era of digitalization and automation, technology has played a pivotal role in shaping logistics operations.
As we look towards the future, technology will continue to shape the logistics landscape. Emerging technologies such as blockchain, robotics, autonomous vehicles, and artificial intelligence hold immense potential to further revolutionize the industry. By embracing these technologies and adopting a forward-thinking approach, logistics providers can gain a competitive edge and meet the evolving demands of the modern supply chain.






