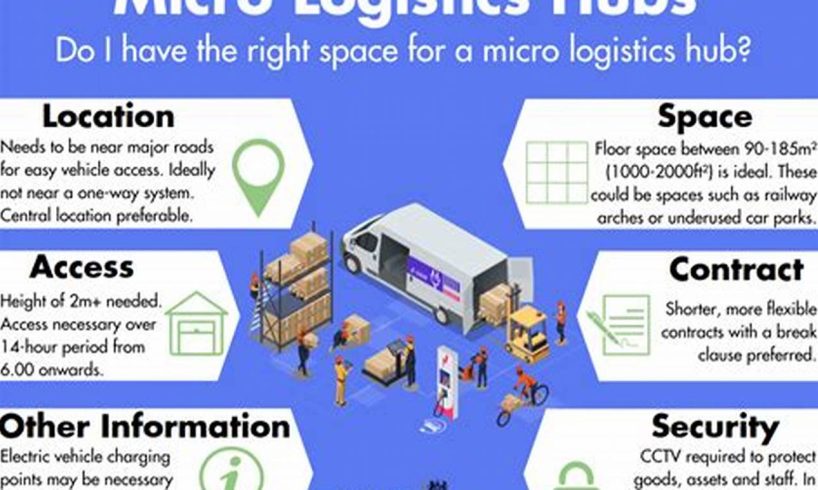
A logistical hub is a central location that serves as a point of storage, distribution, and transportation for goods and materials. It is a vital part of the supply chain, as it allows businesses to efficiently manage their inventory and get products to market quickly and cost-effectively.
Logistical hubs can be located in a variety of places, such as major cities, transportation hubs, or near manufacturing centers. They are typically equipped with state-of-the-art infrastructure, such as warehouses, distribution centers, and transportation terminals. This allows businesses to store their goods in a secure and organized manner, and to quickly and easily ship them to their customers.
Logistical hubs play a critical role in the global economy. They help to ensure that goods and materials are transported efficiently and cost-effectively, which contributes to economic growth and development. In addition, logistical hubs can create jobs and boost local economies. For example, a study by the Brookings Institution found that a new logistical hub in the Chicago area created over 10,000 jobs and generated $1 billion in economic activity.
1. Centralized location
A centralized location is a key component of a logistical hub. It allows businesses to consolidate their inventory and operations in one place, which can lead to significant cost savings and efficiency gains.
- Reduced transportation costs: A centralized location can help businesses reduce their transportation costs by reducing the distance that goods need to be shipped. This is especially important for businesses that ship large volumes of goods or that have customers in multiple locations.
- Improved inventory management: A centralized location can help businesses improve their inventory management by giving them a single point of control over their inventory. This can help businesses reduce their inventory levels and avoid stockouts.
- Increased efficiency: A centralized location can help businesses increase their efficiency by streamlining their operations. This can lead to faster order fulfillment times and improved customer service.
- Flexibility: A centralized location can give businesses the flexibility to respond to changes in demand. For example, if a business experiences a sudden increase in demand, it can easily increase its inventory levels at its centralized location.
Overall, a centralized location is a critical component of a logistical hub. It can help businesses reduce costs, improve efficiency, and increase flexibility.
2. Storage
Storage is a critical component of a logistical hub. It allows businesses to store their inventory in a secure and organized manner, and to quickly and easily ship it to their customers.
- Types of storage: There are a variety of different types of storage available to businesses, including warehouses, distribution centers, and cold storage facilities. The type of storage that a business chooses will depend on the type of products that it stores and its specific needs.
- Inventory management: Inventory management is a key part of storage. Businesses need to be able to track their inventory levels and ensure that they have enough stock to meet customer demand. Inventory management systems can help businesses to optimize their inventory levels and avoid stockouts.
- Security: Storage facilities need to be secure to protect inventory from theft and damage. This can be done through a variety of measures, such as security cameras, alarms, and access control systems.
- Location: The location of a storage facility is important. Businesses need to choose a location that is convenient for their customers and that has good access to transportation.
Overall, storage is a critical component of a logistical hub. It allows businesses to store their inventory in a secure and organized manner, and to quickly and easily ship it to their customers.
3. Distribution
Distribution is a critical component of a logistical hub. It is the process of moving goods from the storage facility to the customer. Distribution can be done through a variety of methods, including trucking, rail, air, and ship.
The choice of distribution method will depend on a number of factors, including the type of product, the distance to the customer, and the cost. For example, trucking is a good option for short distances, while air freight is a good option for long distances.
Distribution is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. Businesses need to work closely with theirto ensure that their products are delivered to their customers on time and in good condition.
The following are some of the benefits of using a logistical hub for distribution:
- Reduced transportation costs
- Improved inventory management
- Increased efficiency
- Flexibility
Overall, distribution is a critical component of a logistical hub. It allows businesses to get their products to market quickly and cost-effectively.
4. Transportation
Transportation is a critical component of a logistical hub, enabling the movement of goods and materials to and from the hub. It plays an integral role in ensuring the efficient flow of products through the supply chain and delivering them to consumers.
- Types of Transportation
Logistical hubs leverage various transportation modes, including trucking, rail, air, and water transportation. The choice of mode depends on factors such as the distance, volume, and nature of the goods being transported. - Infrastructure
Effective transportation requires robust infrastructure, including highways, railways, airports, and seaports. Logistical hubs are often located near major transportation routes to facilitate seamless connectivity and minimize transit times. - Intermodal Transportation
Logistical hubs enable intermodal transportation, where goods are moved using multiple modes of transport. This flexibility optimizes efficiency and cost-effectiveness, allowing businesses to choose the most suitable combination for their specific needs. - Real-Time Tracking
Advanced technologies, such as GPS tracking and sensors, enable real-time monitoring of shipments. This visibility enhances coordination, reduces delays, and improves overall supply chain management.
In summary, transportation is the backbone of logistical hubs, connecting them to markets and facilitating the efficient movement of goods. The integration of various transportation modes, robust infrastructure, and technological advancements contribute to the seamless and cost-effective delivery of products.
5. Inventory management
Inventory management is a critical component of a logistical hub. It involves tracking the quantity and location of inventory, as well as managing the flow of inventory through the hub. Effective inventory management is essential for ensuring that the hub has the right products in the right place at the right time.
There are a number of challenges associated with inventory management in a logistical hub. One challenge is the need to manage a large volume of inventory. Logistical hubs often store thousands of different products, and each product may have multiple SKUs. This can make it difficult to track the quantity and location of all of the inventory.
Another challenge is the need to manage inventory in a dynamic environment. The inventory in a logistical hub is constantly changing. Products are being received and shipped out on a daily basis. This can make it difficult to keep track of the inventory levels and to ensure that the hub has the right products in stock.
Despite the challenges, effective inventory management is essential for the success of a logistical hub. By implementing sound inventory management practices, logistical hubs can improve their efficiency and profitability.
Here are some of the benefits of effective inventory management in a logistical hub:
- Reduced inventory costs
- Improved customer service
- Increased efficiency
- Reduced waste
Overall, inventory management is a critical component of a logistical hub. By implementing sound inventory management practices, logistical hubs can improve their efficiency, profitability, and customer service.
6. Cost-effective
Cost-effectiveness is a critical aspect of logistical hubs. Logistical hubs can help businesses reduce their costs in a number of ways, including:
- Reduced transportation costs: Logistical hubs can help businesses reduce their transportation costs by consolidating their shipments and negotiating lower rates with carriers.
- Reduced inventory costs: Logistical hubs can help businesses reduce their inventory costs by providing them with a central location to store their inventory. This can help businesses reduce their inventory levels and avoid stockouts.
- Reduced labor costs: Logistical hubs can help businesses reduce their labor costs by providing them with access to a pool of skilled labor. This can help businesses reduce their hiring and training costs.
In addition to the cost savings listed above, logistical hubs can also help businesses improve their efficiency and flexibility. This can lead to further cost savings and improved profitability.
Overall, cost-effectiveness is a critical aspect of logistical hubs. Logistical hubs can help businesses reduce their costs, improve their efficiency, and increase their profitability.
7. Efficient
Efficiency is a crucial aspect of logistical hubs. It refers to the ability of a logistical hub to perform its functions in a timely and cost-effective manner, maximizing productivity and minimizing waste.
- Streamlined Processes
Logistical hubs implement streamlined processes and technologies to optimize operations. Automated systems, such as warehouse management systems and inventory tracking software, enhance efficiency by reducing manual labor, minimizing errors, and expediting order fulfillment. - Centralized Operations
By consolidating storage, distribution, and transportation activities in one central location, logistical hubs eliminate redundancies and improve coordination. This centralized approach reduces transit times, optimizes inventory management, and enhances overall supply chain visibility. - Skilled Workforce
Logistical hubs often employ a skilled workforce trained in efficient and distribution practices. These professionals leverage their expertise to maximize space utilization, implement lean methodologies, and continuously improve operations. - Technological Advancements
Logistical hubs embrace technological advancements to enhance efficiency. Radio frequency identification (RFID) technology, for example, enables real-time tracking of inventory, reducing search times and streamlining order fulfillment. Additionally, data analytics tools provide insights into operational patterns, allowing for proactive decision-making and continuous process optimization.
Efficient logistical hubs are essential for businesses to maintain a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced global market. By optimizing processes, centralizing operations, leveraging skilled labor, and embracing technological advancements, logistical hubs facilitate the seamless and cost-effective flow of goods, contributing to increased productivity and profitability.
8. Global reach
Logistical hubs play a critical role in facilitating global trade and expanding the reach of businesses. Their strategic locations and extensive transportation networks enable the efficient movement of goods and materials across borders, connecting suppliers, manufacturers, and consumers worldwide.
- International Connectivity
Logistical hubs serve as gateways to international markets, providing businesses with access to new customers and opportunities for growth. They facilitate the import and export of goods, enabling businesses to tap into global supply chains and distribute their products to a wider audience.
- Reduced Trade Barriers
Logistical hubs help reduce trade barriers by streamlining customs procedures and regulations. They provide centralized facilities and expertise to handle the complex documentation and compliance requirements associated with international trade, making it easier for businesses to navigate the global marketplace.
- Enhanced Supply Chain Visibility
Logistical hubs offer enhanced supply chain visibility through advanced tracking technologies and information systems. This allows businesses to monitor the movement of their goods in real-time, ensuring timely deliveries and reducing the risk of disruptions.
- Cost Optimization
By consolidating shipments and negotiating favorable transportation rates, logistical hubs help businesses optimize their transportation costs. They provide economies of scale and leverage their strategic locations to reduce transit times and associated expenses, making global trade more cost-effective.
The global reach of logistical hubs is essential for businesses to compete in today’s interconnected economy. By providing access to international markets, reducing trade barriers, enhancing supply chain visibility, and optimizing costs, logistical hubs empower businesses to expand their global footprint and drive economic growth.
FAQs on Logistical Hubs
Logistical hubs play a crucial role in the global supply chain, facilitating the efficient movement and distribution of goods. Here are some frequently asked questions to provide further insights into the concept of logistical hubs:
Question 1: What defines a logistical hub?
A logistical hub is a centralized location that serves as a central point for storage, distribution, and transportation of goods. It provides infrastructure, services, and technologies to support the seamless flow of products from suppliers to consumers.
Question 2: What are the key functions of a logistical hub?
Logistical hubs perform various functions, including inventory management, order fulfillment, transportation coordination, and value-added services such as packaging and labeling. They aim to optimize the supply chain process and enhance efficiency.
Question 3: How do logistical hubs benefit businesses?
Businesses utilizing logistical hubs can gain advantages such as reduced transportation costs, improved inventory management, enhanced supply chain visibility, and access to global markets. These hubs provide a competitive edge by streamlining operations and optimizing resource allocation.
Question 4: What are the different types of logistical hubs?
Logistical hubs can be classified based on their location, size, and specialization. Some common types include regional hubs, national hubs, and international hubs. Each type serves a specific geographic region or industry.
Question 5: How are logistical hubs evolving in the digital age?
Logistical hubs are embracing digital technologies to enhance their operations. Automation, data analytics, and blockchain are transforming hub management, leading to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and increased transparency.
Question 6: What are the future trends in logistical hub development?
Future trends in logistical hub development include a focus on sustainability, smart technologies, and resilience. Hubs will prioritize eco-friendly practices, leverage IoT and AI for optimization, and enhance infrastructure to mitigate supply chain disruptions.
By understanding the fundamentals and key aspects of logistical hubs, businesses can leverage their capabilities to optimize their supply chain strategies and gain a competitive advantage in today’s globalized marketplace.
Proceed to the next section to explore the benefits of logistical hubs in greater detail.
Define Logistical Hub
To effectively understand the concept of a logistical hub, consider the following tips:
Tip 1: Grasp the Core Functions
Recognize that logistical hubs centralize storage, distribution, and transportation activities. They facilitate the movement of goods from suppliers to consumers, optimizing the supply chain process.
Tip 2: Understand the Benefits
Understand that logistical hubs offer advantages such as reduced transportation costs, improved inventory management, and enhanced supply chain visibility. They provide businesses with a competitive edge and streamline operations.
Tip 3: Distinguish Hub Types
Recognize that logistical hubs vary in size, location, and specialization. Regional hubs serve specific geographic areas, while national and international hubs cater to broader regions or global markets.
Tip 4: Embrace Digital Advancements
Be aware that logistical hubs are embracing digital technologies to enhance efficiency and transparency. Automation, data analytics, and blockchain are transforming hub management, leading to improved outcomes.
Tip 5: Consider Future Trends
Stay informed about emerging trends in logistical hub development. Focus on sustainability, smart technologies, and resilience to gain insights into the future direction of this industry.
By incorporating these tips, you can deepen your understanding of logistical hubs and their significance in the global supply chain.
Proceed to the next section to explore the benefits of logistical hubs in greater detail.
Conclusion: Understanding the Significance of Logistical Hubs
In summation, logistical hubs serve as vital cogs in the global supply chain, facilitating the efficient movement and distribution of goods. They provide businesses with a competitive edge by optimizing transportation, inventory management, and supply chain visibility. As we progress into the future, logistical hubs will continue to evolve, embracing digital technologies and sustainable practices to meet the demands of a dynamic global economy.
The ongoing development of logistical hubs underscores their increasing importance in international trade and economic growth. By understanding the concept and benefits of logistical hubs, businesses and policymakers can make informed decisions to leverage their capabilities and drive economic prosperity.






