Population models are important tools for conserving endangered species. They help us to understand how populations grow and decline, and to predict how they will respond to different management actions. There are two main types of population models: logistic and exponential. Logistic models assume that population growth is limited by environmental factors, such as food and habitat. Exponential models assume that population growth is unlimited. For discussion about population model used for conserving endangered species, logistic or exponential is the keyword term we use to this article.
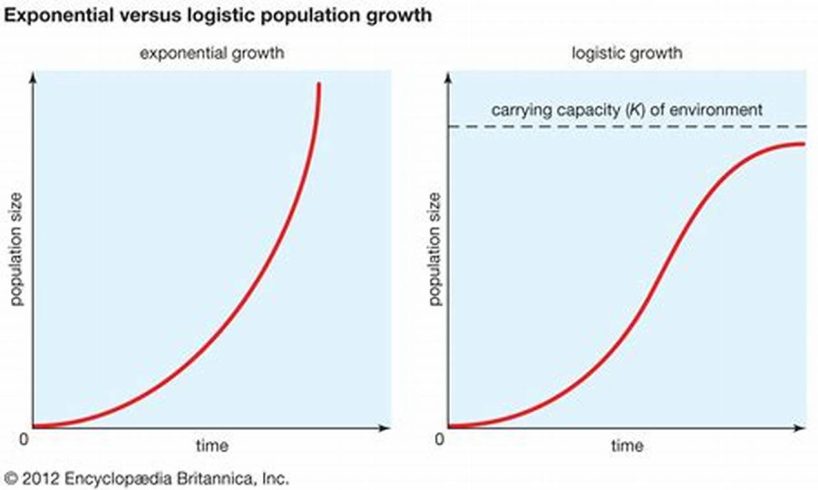
Logistic models are often used to model the growth of populations that are close to their carrying capacity. Carrying capacity is the maximum population size that can be supported by the environment. Exponential models are often used to model the growth of populations that are not close to their carrying capacity.
Population models can be used to predict the impact of different management actions on endangered species. For example, a model could be used to predict the impact of a new conservation program on the population of a particular species. Models can also be used to identify the most effective management actions for conserving endangered species.Logistic or exponential models are widely used when dealing with endangered species and population studies.
1. Population growth
Population growth is a key factor in population models used for conserving endangered species. Population models help us to understand how populations grow and decline, and to predict how they will respond to different management actions. Population growth is determined by a number of factors, including birth rate, death rate, and immigration and emigration rates. For discussion about population model used for conserving endangered species, logistic or exponential is the keyword term we use to this article.
Understanding population growth is important for conserving endangered species because it allows us to identify populations that are at risk of decline. It also helps us to develop management strategies to increase population growth and to recover endangered species.
For example, if a population of endangered species is experiencing low population growth, a management strategy could be implemented to increase the birth rate or to reduce the death rate. This could involve Manahmen such as providing food and habitat for the species, or reducing the number of predators.
Population models are an important tool for conserving endangered species. They help us to understand how populations grow and decline, and to predict how they will respond to different management actions. Understanding population growth is a key factor in developing effective conservation strategies.
2. Carrying capacity
Carrying capacity is the maximum population size that can be supported by a given environment. It is an important concept in population ecology and conservation biology, as it helps us to understand the limits of population growth and the potential for species to recover from decline. Carrying capacity is determined by a number of factors, including the availability of food, water, habitat, and other resources.
Population models that are used for conserving endangered species often incorporate carrying capacity as a key parameter. This is because carrying capacity can help us to predict how a population will respond to different management actions. For example, if a population is below carrying capacity, then it is likely to grow in response to management actions that increase the availability of resources. However, if a population is at or near carrying capacity, then it is less likely to respond to management actions that increase resources. Population model used for conserving endangered species logistic or exponential is the keyword term we use to this article.
Understanding carrying capacity is important for conserving endangered species because it helps us to set realistic goals for population recovery. It also helps us to identify the factors that are limiting population growth and to develop management strategies to address these factors. For example, if a population of endangered species is limited by the availability of food, then a management strategy could be implemented to increase the amount of food available to the species.
Carrying capacity is a complex concept, but it is an important one for understanding population growth and decline. By incorporating carrying capacity into population models, we can improve our ability to conserve endangered species.
3. Environmental factors
Environmental factors play a crucial role in population models used for conserving endangered species. These factors can influence the growth, decline, and recovery of populations. Population model used for conserving endangered species logistic or exponential is the keyword term we use to this article. Understanding the connection between environmental factors and population models is essential for developing effective conservation strategies.
Population models that incorporate environmental factors can help us to predict how populations will respond to changes in their environment. For example, a model could be used to predict how a population of endangered species would respond to climate change. The model could take into account factors such as changes in temperature, precipitation, and sea level. This information could then be used to develop management strategies to help the species adapt to climate change.
Real-life examples demonstrate the importance of considering environmental factors in population models. For instance, the decline of the northern spotted owl population in the Pacific Northwest was linked to the loss of old-growth forests. Old-growth forests provide the nesting habitat that the owls require. By incorporating this environmental factor into a population model, researchers were able to predict the impact of logging on the owl population. This information was used to develop conservation strategies to protect old-growth forests and help the owl population recover.
Understanding the connection between environmental factors and population models is essential for conserving endangered species. By incorporating environmental factors into population models, we can improve our ability to predict how populations will respond to changes in their environment. This information can be used to develop more effective conservation strategies and to help endangered species recover.
4. Logistic models
Logistic models are a type of population model that is used to describe the growth of populations that are limited by environmental factors. These models are often used to model the growth of populations of endangered species. Population model used for conserving endangered species logistic or exponential is the keyword term we use to this article. Logistic models take into account the carrying capacity of the environment, which is the maximum population size that can be supported by the environment. Carrying capacity is determined by a number of factors, including the availability of food, water, habitat, and other resources.
Logistic models are important for conserving endangered species because they can help us to predict how populations will respond to different management actions. For example, a logistic model could be used to predict how a population of endangered species would respond to a new conservation program. The model could take into account factors such as the carrying capacity of the environment, the birth rate and death rate of the species, and the impact of the conservation program on these factors. This information could then be used to develop management strategies to help the species recover.
Logistic models have been used to successfully conserve a number of endangered species. For example, logistic models were used to help develop conservation strategies for the black-footed ferret, the California condor, and the giant panda. These models helped to identify the factors that were limiting the recovery of these species and to develop management strategies to address these factors. As a result, these species have all made significant recoveries in recent years.
Logistic models are a valuable tool for conserving endangered species. They can help us to understand how populations grow and decline, and to predict how they will respond to different management actions. This information can be used to develop more effective conservation strategies and to help endangered species recover.
5. Exponential models
Exponential models are a type of population model that is used to describe the growth of populations that are not limited by environmental factors. These models assume that the population growth rate is constant, and that the population will continue to grow exponentially until it reaches infinity. Population model used for conserving endangered species logistic or exponential is the keyword term we use to this article. Exponential models are often used to model the growth of populations of invasive species, which are species that have been introduced to a new environment and have no natural predators or competitors.
Exponential models can be used to predict the impact of invasive species on native species. For example, a model could be used to predict how a population of invasive species would grow if it were introduced to a new ecosystem. The model could take into account factors such as the growth rate of the invasive species, the carrying capacity of the new ecosystem, and the impact of the invasive species on native species. This information could then be used to develop management strategies to control the spread of the invasive species and to protect native species.
Exponential models have also been used to model the growth of populations of endangered species. For example, a model could be used to predict how a population of endangered species would grow if it were given protection from hunting or habitat destruction. The model could take into account factors such as the birth rate and death rate of the species, the carrying capacity of the environment, and the impact of protection on these factors. This information could then be used to develop management strategies to help the species recover.
Exponential models are a valuable tool for conserving endangered species. They can help us to understand how populations grow and decline, and to predict how they will respond to different management actions. This information can be used to develop more effective conservation strategies and to help endangered species recover.
6. Conservation programs
Conservation programs play a crucial role in the conservation of endangered species. Population models used for conserving endangered species, whether logistic or exponential, provide valuable insights for developing effective conservation programs. These models help to predict population trends, assess the impact of conservation interventions, and evaluate the likelihood of species recovery.
- Habitat protection and restoration: Population models can identify critical habitats for endangered species and assess the impact of habitat loss and fragmentation. This information can inform conservation programs aimed at protecting and restoring habitats to support viable populations.
- Population monitoring: Population models can be used to design monitoring programs to track population trends and identify threats. This information is essential for adaptive management and making informed decisions about conservation interventions.
- Reintroduction and translocation: Population models can help to determine the feasibility of reintroducing or translocating endangered species to new areas. They can predict the likelihood of population establishment and growth, and identify suitable release sites.
- Captive breeding and genetic management: Population models can inform captive breeding programs by providing insights into the genetic diversity and demographic parameters of endangered species. They can also help to design genetic management strategies to maintain genetic variation and prevent inbreeding depression.
By integrating population models into conservation programs, we can enhance our ability to conserve endangered species and ensure their long-term survival. These models provide a quantitative framework for evaluating conservation strategies, predicting population responses, and making informed decisions to protect and recover endangered species.
7. Management actions
Management actions are essential for conserving endangered species and ensuring their long-term survival. Population models used for conserving endangered species, whether logistic or exponential, provide valuable insights for developing and evaluating management actions. These models help to predict population responses to different interventions and assess the effectiveness of conservation strategies.
- Habitat management: Population models can identify critical habitats for endangered species and assess the impact of habitat loss and fragmentation. This information can inform management actions aimed at protecting and restoring habitats to support viable populations. For example, a population model could be used to predict the impact of a proposed development on the habitat of an endangered bird species. The model could then be used to identify alternative development plans that would minimize the impact on the bird’s habitat.
- Population management: Population models can be used to design and evaluate population management strategies, such as captive breeding programs, reintroductions, and translocations. These models can help to predict the likelihood of population establishment and growth, and identify suitable release sites. For example, a population model could be used to determine the number of individuals that need to be released in a reintroduction program to ensure a high probability of success.
- Threat management: Population models can be used to assess the impact of threats to endangered species, such as hunting, poaching, and disease. This information can inform management actions aimed at reducing or eliminating these threats. For example, a population model could be used to predict the impact of a proposed hunting ban on the population of an endangered antelope species.
- Monitoring and adaptive management: Population models can be used to design and evaluate monitoring programs to track population trends and identify threats. This information is essential for adaptive management and making informed decisions about conservation interventions. For example, a population model could be used to track the progress of a reintroduction program and identify any factors that are limiting the success of the program.
By integrating population models into management actions, we can enhance our ability to conserve endangered species and ensure their long-term survival. These models provide a quantitative framework for evaluating conservation strategies, predicting population responses, and making informed decisions to protect and recover endangered species.
8. Population viability
Population viability refers to the likelihood that a population will persist over time. It is a key concept in conservation biology, as it helps us to identify populations that are at risk of extinction and to develop management strategies to help them recover. Population model used for conserving endangered species logistic or exponential is the keyword term we use to this article. Population models are an important tool for assessing population viability. They can be used to predict how populations will respond to different threats, such as habitat loss, hunting, and climate change. This information can then be used to develop management strategies to help populations persist in the face of these threats.
There are a number of factors that can affect population viability, including population size, genetic diversity, and habitat quality. Small populations are more vulnerable to extinction than large populations, as they are more likely to be affected by random events, such as disease outbreaks or natural disasters. Populations with low genetic diversity are also more vulnerable to extinction, as they are less able to adapt to changes in their environment. Habitat quality is also important for population viability, as it provides the resources that populations need to survive and reproduce.
Population models can be used to assess the impact of different factors on population viability. For example, a population model could be used to predict how a population of endangered species would respond to a new conservation program. The model could take into account factors such as the population’s size, genetic diversity, habitat quality, and the impact of the conservation program on these factors. This information could then be used to develop management strategies to help the population recover.
Population viability is a complex concept, but it is an important one for conservation biology. Population models are a valuable tool for assessing population viability and developing management strategies to help endangered species recover.
FAQs on Population Models for Conserving Endangered Species
Population models play a crucial role in conserving endangered species. They help us understand how populations grow and decline, and predict how they will respond to different management actions. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about population models in the context of endangered species conservation.
Question 1: What types of population models are used for conserving endangered species?
There are two main types of population models used for conserving endangered species: logistic models and exponential models. Logistic models assume that population growth is limited by environmental factors, such as food and habitat. Exponential models assume that population growth is unlimited.
Question 2: How do population models help in developing conservation strategies?
Population models can help conservationists predict how populations will respond to different management actions. For example, a model could be used to predict how a population of endangered species would respond to a new conservation program. The model could take into account factors such as the population’s size, genetic diversity, habitat quality, and the impact of the conservation program on these factors.
Question 3: What factors are considered when using population models for endangered species conservation?
Factors considered when using population models for endangered species conservation include population size, genetic diversity, habitat quality, carrying capacity, environmental factors, and potential threats.
Question 4: Are population models always accurate in predicting population trends?
Population models are not always accurate in predicting population trends. They are based on assumptions and simplifications, and the accuracy of the predictions depends on the quality of the data used to develop the model. However, population models provide valuable insights into population dynamics and can help inform conservation decisions.
Question 5: How can population models be improved to enhance their accuracy?
Population models can be improved by incorporating more detailed data, such as spatial data and genetic information. Additionally, using more sophisticated modeling techniques and considering a wider range of scenarios can also improve the accuracy of population models.
Question 6: What are the limitations of population models in endangered species conservation?
Population models have limitations, including their reliance on assumptions and simplifications. They may not account for all the complexities of real-world populations and ecosystems. Additionally, population models require accurate data, which may not always be available.
Despite their limitations, population models are valuable tools for conserving endangered species. They provide insights into population dynamics and help inform conservation decisions. By understanding the strengths and limitations of population models, conservationists can use them effectively to protect and recover endangered species.
For further exploration, refer to the following article sections:
- Population Growth
- Carrying Capacity
- Environmental Factors
- Logistic Models
- Exponential Models
- Conservation Programs
- Management Actions
- Population Viability
Tips for Using Population Models in Endangered Species Conservation
Population models are valuable tools for conserving endangered species. They can help us understand how populations grow and decline, and predict how they will respond to different management actions. However, it is important to use population models wisely and to be aware of their limitations.
Tip 1: Use the appropriate model type.
There are two main types of population models: logistic models and exponential models. Logistic models assume that population growth is limited by environmental factors, such as food and habitat. Exponential models assume that population growth is unlimited. The choice of model type depends on the specific situation being modeled.
Tip 2: Use accurate and reliable data.
The accuracy of population models depends on the quality of the data used to develop them. It is important to use data that is accurate, reliable, and relevant to the species and ecosystem being modeled.
Tip 3: Consider the limitations of population models.
Population models are simplifications of real-world systems. They do not account for all of the complexities of population dynamics and ecosystems. It is important to be aware of the limitations of population models and to interpret their results with caution.
Tip 4: Use population models in conjunction with other conservation tools.
Population models are not the only tool that should be used for conserving endangered species. They should be used in conjunction with other conservation tools, such as habitat protection, population monitoring, and captive breeding programs.
Tip 5: Seek expert advice.
If you are not familiar with population modeling, it is important to seek expert advice. Population models can be complex, and it is important to use them correctly in order to get meaningful results.
By following these tips, you can use population models to help conserve endangered species and protect biodiversity.
Summary of key takeaways:
- Population models are valuable tools for conserving endangered species.
- There are two main types of population models: logistic models and exponential models.
- It is important to use the appropriate model type and accurate data.
- Population models have limitations and should be used in conjunction with other conservation tools.
- Seeking expert advice can help you use population models effectively.
Conclusion:
Population models can be powerful tools for conserving endangered species. By using population models wisely and in conjunction with other conservation tools, we can help to protect and recover endangered species populations.
Conclusion
Population models play a crucial role in the conservation of endangered species. They provide valuable insights into population dynamics, enabling us to predict population responses to various threats and management actions. By utilizing logistic or exponential models, we can assess population growth, carrying capacity, environmental factors, and other key aspects that influence species recovery.
The integration of population models into conservation strategies strengthens our ability to protect and restore endangered species. These models guide habitat protection and restoration efforts, inform population management decisions, and aid in threat mitigation. They also facilitate monitoring and adaptive management, ensuring that conservation actions are effective and responsive to changing conditions.
As we continue to face the challenges of biodiversity loss and climate change, population models will remain indispensable tools for conserving endangered species. By embracing these models and incorporating them into our conservation strategies, we can work towards a future where all species have a chance to thrive.






