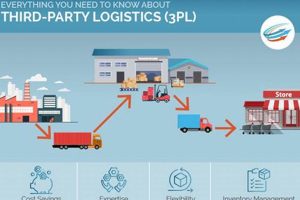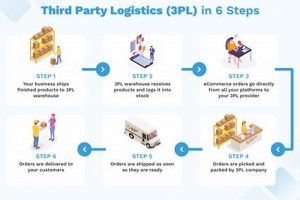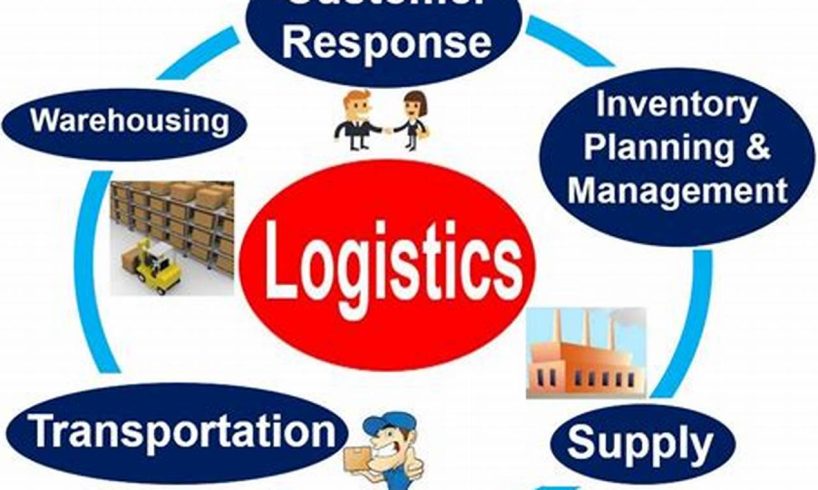
Service logistics, as a specialized discipline, involves the efficient and effective flow of services from the point of origin to the point of consumption, ensuring that the right service is delivered to the right customer at the right time and place, at an optimal cost. Unlike traditional logistics that deal with physical goods, service logistics focuses on the movement and delivery of intangible services, such as consulting, healthcare, education, and financial services.
Service logistics plays a vital role in today’s economy, as service industries account for a significant portion of the GDP in developed countries. The effective management of service logistics can lead to improved customer satisfaction, reduced costs, and increased efficiency. It also ensures that service providers can meet the ever-changing demands of customers in a timely and cost-effective manner.
The main article will explore the various aspects of service logistics, including the different types of services, the challenges involved in service logistics management, and the latest trends and technologies that are shaping the future of service logistics.
1. Intangibility
The intangibility of services presents a unique challenge in service logistics, as it makes it difficult to manage and measure the delivery of services. Unlike physical goods, services cannot be seen, touched, or inventoried. This makes it challenging to track their progress through the supply chain and to ensure that they are delivered to customers in a timely and efficient manner.
To address this challenge, service logistics managers must rely on a variety of performance metrics to measure the quality of service delivery. These metrics may include customer satisfaction surveys, response times, and error rates. By tracking these metrics, service logistics managers can identify areas for improvement and ensure that services are meeting the needs of customers.
The intangibility of services also has implications for the way that service logistics is managed. Traditional logistics methods, such as inventory management and transportation, are not always applicable to services. Instead, service logistics managers must focus on developing strategies that ensure the efficient and effective delivery of services, while also taking into account the unique characteristics of services.
2. Heterogeneity
The heterogeneity of services presents a significant challenge for service logistics managers, as it makes it difficult to standardize the delivery of services. Unlike physical goods, which can be produced and delivered in a standardized manner, services are often customized to meet the specific needs of individual customers. This variability makes it challenging to develop efficient and effective service logistics strategies.
To address this challenge, service logistics managers must focus on developing flexible and adaptable strategies that can accommodate the variability of services. This may involve developing modular service offerings that can be customized to meet the specific needs of customers, or developing service delivery processes that can be tailored to different customer requirements. Additionally, service logistics managers must work closely with customers to understand their specific needs and to develop service delivery strategies that meet those needs.
The heterogeneity of services also has implications for the way that service logistics is managed. Traditional logistics methods, such as inventory management and transportation, are not always applicable to services. Instead, service logistics managers must focus on developing strategies that ensure the efficient and effective delivery of services, while also taking into account the unique characteristics of services.
3. Perishability
The perishability of services is a key aspect of service logistics definition, as it has a significant impact on the way that services are delivered. Unlike physical goods, which can be stored and delivered at a later date, services must be delivered immediately. This creates a number of challenges for service logistics managers, as they must ensure that services are delivered to customers in a timely and efficient manner.
- Immediate Delivery: The perishability of services means that they must be delivered to customers immediately. This requires service logistics managers to develop strategies that ensure that services are delivered to customers as quickly as possible. This may involve using expedited shipping methods or developing innovative delivery channels.
- Capacity Planning: The perishability of services also makes it important for service logistics managers to plan for capacity. This involves forecasting demand for services and ensuring that there are sufficient resources in place to meet that demand. This may involve hiring additional staff or investing in new equipment.
- Flexibility: The perishability of services also requires service logistics managers to be flexible. This means being able to adapt to changes in demand and to develop contingency plans in case of disruptions. This may involve developing partnerships with other service providers or investing in technology that can help to automate service delivery.
- Customer Expectations: The perishability of services also has an impact on customer expectations. Customers expect services to be delivered immediately, and they may be dissatisfied if they have to wait for a service to be delivered. This means that service logistics managers must focus on developing strategies that meet the expectations of customers.
The perishability of services is a key challenge for service logistics managers. However, by understanding the challenges and developing effective strategies, service logistics managers can ensure that services are delivered to customers in a timely and efficient manner.
4. Simultaneity
In service logistics, the concept of simultaneity plays a pivotal role, as services are often produced and consumed at the same time. Unlike physical goods, which can be produced in advance and stored until they are needed, services are typically intangible and must be delivered in real-time. This characteristic introduces unique challenges and opportunities in the management of service logistics.
- Real-Time Delivery: The simultaneous nature of services requires that they be delivered in real-time. This means that service logistics providers must have the capability to deliver services quickly and efficiently, often within tight timeframes. This may involve using expedited shipping methods or developing innovative delivery channels.
- Capacity Planning: The simultaneity of services also makes it important for service logistics providers to plan for capacity. This involves forecasting demand for services and ensuring that there are sufficient resources in place to meet that demand. This may involve hiring additional staff or investing in new equipment.
- Customer Interaction: The simultaneous nature of services also requires close coordination between providers and customers. This is because customers are often actively involved in the service delivery process, and their feedback and input can have a significant impact on the quality of the service. This means that service logistics providers must develop strategies that facilitate effective communication and collaboration with customers.
- Technology: Technology can play a vital role in enabling the simultaneous delivery of services. For example, online platforms can be used to facilitate real-time communication between providers and customers, and automated systems can be used to streamline service delivery processes.
The simultaneity of services is a key aspect of service logistics definition. By understanding the challenges and opportunities associated with simultaneity, service logistics providers can develop effective strategies that ensure the efficient and effective delivery of services.
5. Customer involvement
Customer involvement is a key aspect of service logistics definition, as it recognizes the active role that customers play in the service delivery process. Unlike physical goods, which can be delivered to customers without their direct involvement, services often require the active participation of customers. This involvement can take many forms, such as providing information, feedback, or even co-creating the service itself.
The involvement of customers in the service delivery process has a significant impact on the quality of the service. When customers are actively involved, they can provide valuable insights and feedback that can help service providers to improve the quality of their services. Additionally, customer involvement can help to create a sense of ownership and buy-in, which can lead to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
There are many ways that service logistics providers can encourage customer involvement in the service delivery process. For example, service providers can use surveys, focus groups, and other methods to gather customer feedback. Additionally, service providers can develop self-service tools that allow customers to track the progress of their service requests and to provide feedback on the quality of the service.
By understanding the importance of customer involvement and by developing strategies to encourage customer involvement, service logistics providers can improve the quality of their services and increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Here are some real-life examples of how customer involvement has impacted the quality of service delivery:
- A restaurant that asks customers for feedback on their meals and uses that feedback to improve its menu and service.
- A hotel that allows customers to check in and out online, giving them more control over their stay.
- A bank that offers customers the ability to track their account balances and transactions online, giving them greater visibility into their finances.
These are just a few examples of how customer involvement can improve the quality of service delivery. By understanding the importance of customer involvement and by developing strategies to encourage customer involvement, service logistics providers can improve the quality of their services and increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
6. Technology
Technology plays a crucial role in service logistics definition, as it enables efficient delivery and customer engagement. The use of technology in service logistics has transformed the way services are delivered and consumed, leading to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and increased customer satisfaction.
One of the most significant benefits of technology in service logistics is its ability to improve efficiency. Technology can be used to automate many tasks that were previously done manually, such as order processing, inventory management, and customer support. This can free up service providers to focus on more value-added activities, such as developing new services and improving customer relationships.
Technology also plays a vital role in customer engagement. By providing customers with access to self-service tools and online platforms, service providers can empower customers to manage their own accounts, track the progress of their orders, and get support when they need it. This can lead to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Here are some real-life examples of how technology is being used to improve service logistics:
- Uber uses a mobile app to connect riders with drivers, making it easy for people to get a ride whenever they need one.
- Amazon uses a sophisticated logistics network to deliver millions of packages to customers every day.
- Netflix uses a streaming platform to deliver movies and TV shows to customers on demand.
These are just a few examples of how technology is transforming service logistics. By continuing to invest in technology, service providers can improve the efficiency of their operations, increase customer engagement, and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
7. Sustainability
Sustainability is a critical aspect of service logistics definition, as it ensures the long-term viability of service organizations and the well-being of society as a whole. Service logistics activities have environmental and social impacts, and it is essential for organizations to consider these impacts and take steps to minimize their negative effects.
- Environmental Sustainability
Service logistics activities can have a significant impact on the environment. For example, transportation of goods and people can contribute to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Service organizations can reduce their environmental impact by using more sustainable modes of transportation, such as electric vehicles or public transportation. Additionally, service organizations can use renewable energy sources to power their operations and reduce their carbon footprint.
- Social Sustainability
Service logistics activities can also have a social impact. For example, the way that goods and services are delivered can affect the quality of life for local communities. Service organizations can improve their social sustainability by considering the needs of local communities and working to minimize the negative impacts of their operations. Additionally, service organizations can support local businesses and create jobs in the communities they serve.
By considering environmental and social sustainability, service logistics organizations can ensure their long-term viability and contribute to the well-being of society as a whole.
FAQs on Service Logistics Definition
This section aims to address common questions and clarify misconceptions surrounding service logistics definition, providing a comprehensive understanding of this crucial concept.
Question 1: What is the core concept behind service logistics?
Service logistics focuses on the effective and efficient flow of services from the point of origin to the point of consumption, ensuring the right service is delivered to the right customer at the right time and place, at an optimal cost.
Question 2: How does service logistics differ from traditional logistics?
Unlike traditional logistics that deals with physical goods, service logistics deals with the movement and delivery of intangible services, such as consulting, healthcare, education, and financial services.
Question 3: What are the key characteristics of services that impact service logistics?
Services are intangible, heterogeneous, perishable, and often involve simultaneous production and consumption, requiring close customer involvement.
Question 4: Why is customer involvement crucial in service logistics?
Customer involvement significantly impacts service quality, as customers provide valuable insights, feedback, and co-create the service, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty.
Question 5: How does technology contribute to service logistics?
Technology plays a vital role in service logistics, enabling efficient delivery, improving customer engagement, and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Question 6: Why is sustainability important in service logistics?
Sustainability ensures long-term viability by minimizing the environmental and social impacts of service logistics activities, contributing to the well-being of society.
In summary, service logistics definition encompasses the efficient and effective management of service delivery, considering the unique characteristics of services and leveraging technology and sustainability to drive customer satisfaction and organizational success.
Moving forward, the main article will delve deeper into the various aspects of service logistics, providing a comprehensive exploration of this dynamic and essential field.
Tips on Service Logistics Definition
Service logistics definition encompasses the efficient and effective management of service delivery, considering the unique characteristics of services and leveraging technology and sustainability to drive customer satisfaction and organizational success.
Tip 1: Understand the Core Concept
– Grasp the fundamental concept of service logistics as the flow of services from origin to consumption, ensuring timely, cost-effective delivery to customers. Tip 2: Differentiate from Traditional Logistics
– Recognize that service logistics deals with intangible services, unlike traditional logistics which focuses on physical goods. Tip 3: Consider Key Service Characteristics
– Understand the impact of intangibility, heterogeneity, perishability, simultaneity, and customer involvement on service logistics management. Tip 4: Leverage Customer Involvement
– Engage customers actively in the service delivery process to enhance quality, satisfaction, and loyalty. Tip 5: Embrace Technology for Efficiency
– Utilize technology to automate tasks, improve customer engagement, and enhance operational efficiency in service logistics. Tip 6: Prioritize Sustainability
– Integrate environmental and social sustainability into service logistics to ensure long-term viability and contribute to societal well-being. Tip 7: Focus on Customer Value
– Tailor service logistics strategies to deliver value to customers, meeting their specific needs and expectations. Tip 8: Monitor and Measure Performance
– Establish metrics and monitor performance to identify areas for improvement and optimize service logistics operations.
By following these tips, organizations can refine their understanding of service logistics definition and develop effective strategies to enhance service delivery, customer satisfaction, and overall business success.
Moving forward, the main article will delve deeper into the various aspects of service logistics, providing a comprehensive exploration of this dynamic and essential field.
Conclusion
This article has explored the multifaceted concept of service logistics definition, shedding light on its key aspects, implications, and significance in today’s service-oriented economy. By understanding the unique characteristics of services and the challenges they pose to logistics management, organizations can develop effective strategies to deliver value to customers, optimize operations, and achieve sustainable growth.
Service logistics is not merely about moving services from point A to point B; it encompasses a complex interplay of customer involvement, technology adoption, and sustainability considerations. By embracing these principles and leveraging the latest advancements in the field, organizations can transform their service logistics operations into a competitive advantage, driving customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and long-term success.