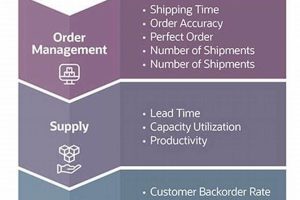
Maintenance and logistics tracking is the process of monitoring and managing the maintenance and logistics of an organization’s assets and resources. It involves tracking the location, condition, and maintenance history of assets, as well as the movement of goods and materials through the supply chain. Maintenance and logistics tracking can be done manually or with the help of specialized software.
Effective maintenance and logistics tracking can help organizations to improve their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. It can also help organizations to comply with regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
Here are some of the benefits of maintenance and logistics tracking:
- Improved asset utilization
- Reduced maintenance costs
- Improved customer satisfaction
- Enhanced regulatory compliance
There are a number of different ways to implement maintenance and logistics tracking, and the best approach will vary depending on the size and complexity of the organization. However, some common methods include:
- Manual tracking: This involves using spreadsheets, databases, or other manual methods to track asset and logistics information.
- Automated tracking: This involves using specialized software to automate the tracking of asset and logistics information. Automated tracking systems can be more efficient and accurate than manual tracking systems.
Regardless of the method used, maintenance and logistics tracking is an essential part of any organization’s operations. By effectively tracking its assets and logistics, organizations can improve their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
1. Asset management
Asset management is the process of tracking and managing the assets of an organization. This includes tracking the location, condition, and maintenance history of assets, as well as the movement of assets through the supply chain. Asset management is a critical component of maintenance and logistics tracking, as it provides the foundation for effective maintenance and logistics planning.
For example, by tracking the maintenance history of assets, organizations can identify patterns of failure and take steps to prevent them from recurring. This can help to reduce downtime and improve productivity. Additionally, by tracking the movement of assets through the supply chain, organizations can identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, and take steps to improve the flow of goods.
Asset management is also important for regulatory compliance and financial reporting. Many organizations are required to track and report on their assets for financial and tax purposes. Asset management can also help organizations to comply with environmental regulations, such as those governing the disposal of hazardous materials.
2. Inventory control
Inventory control is the process of managing the inventory of an organization. This includes tracking the quantity, location, and condition of inventory items, as well as the movement of inventory items through the supply chain. Inventory control is a critical component of maintenance and logistics tracking, as it provides the foundation for effective maintenance and logistics planning.
For example, by tracking the quantity of inventory items, organizations can identify when inventory levels are low and need to be replenished. This can help to prevent stockouts and ensure that maintenance and logistics operations can continue uninterrupted. Additionally, by tracking the location of inventory items, organizations can identify where inventory is located and how it can be moved to where it is needed most. This can help to reduce lead times and improve the efficiency of maintenance and logistics operations.
Inventory control is also important for regulatory compliance and financial reporting. Many organizations are required to track and report on their inventory for financial and tax purposes. Inventory control can also help organizations to comply with environmental regulations, such as those governing the disposal of hazardous materials.
3. Work order management
Work order management is a critical component of maintenance and logistics tracking. It involves the process of creating, assigning, tracking, and completing work orders for maintenance and logistics tasks. Work order management systems can be used to track the status of work orders, assign tasks to technicians, and generate reports on work order activity.
- Scheduling
Work order management systems can be used to schedule work orders for specific dates and times. This can help to ensure that maintenance and logistics tasks are completed on time and without disruption to operations.
- Tracking
Work order management systems can be used to track the status of work orders in real time. This can help to identify any delays or problems that may occur during the maintenance or logistics process.
- Reporting
Work order management systems can be used to generate reports on work order activity. This information can be used to identify trends and patterns, and to improve the efficiency of maintenance and logistics operations.
- Integration
Work order management systems can be integrated with other enterprise systems, such as asset management systems and inventory control systems. This can help to streamline the maintenance and logistics process and improve the overall efficiency of the organization.
Effective work order management can help to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of maintenance and logistics operations. It can also help to reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
4. Preventive maintenance
Preventive maintenance is a maintenance strategy that involves regularly inspecting and servicing equipment to prevent breakdowns and failures. It is an important component of maintenance and logistics tracking, as it can help to identify and address potential problems before they cause major disruptions to operations.
Preventive maintenance can be performed on a variety of equipment, including machinery, vehicles, and buildings. The specific tasks involved in preventive maintenance will vary depending on the type of equipment being serviced. However, some common tasks include:
- Inspecting equipment for signs of wear and tear
- Cleaning and lubricating equipment
- Replacing worn or damaged parts
- Performing minor repairs
By performing preventive maintenance on a regular basis, organizations can help to improve the reliability and lifespan of their equipment. This can lead to reduced downtime, improved productivity, and lower maintenance costs. Additionally, preventive maintenance can help to identify and address potential safety hazards, which can help to protect employees and customers.
Maintenance and logistics tracking can help organizations to implement and manage preventive maintenance programs. By tracking the maintenance history of equipment, organizations can identify patterns of failure and develop preventive maintenance schedules that are tailored to the specific needs of their equipment. Additionally, maintenance and logistics tracking systems can be used to track the progress of preventive maintenance tasks and to generate reports on the effectiveness of preventive maintenance programs.
5. Predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance is a maintenance strategy that uses data and analytics to predict when equipment is likely to fail. This information can then be used to schedule maintenance tasks before the equipment fails, preventing unplanned downtime and costly repairs.
- Data collection
The first step in predictive maintenance is to collect data from equipment. This data can include information such as temperature, vibration, and power consumption. Data can be collected using sensors that are attached to the equipment.
- Data analysis
Once data has been collected, it must be analyzed to identify patterns and trends. This can be done using a variety of statistical techniques. Data analysis can be used to identify equipment that is at risk of failure and to predict when that failure is likely to occur.
- Scheduling maintenance
Once equipment has been identified as being at risk of failure, maintenance can be scheduled to address the issue before the equipment fails. This can help to prevent unplanned downtime and costly repairs.
- Benefits of predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance can provide a number of benefits, including:
- Reduced downtime
- Improved equipment reliability
- Lower maintenance costs
- Increased productivity
Predictive maintenance is a powerful tool that can help organizations to improve their maintenance and logistics operations. By using data and analytics to predict when equipment is likely to fail, organizations can schedule maintenance tasks before the equipment fails, preventing unplanned downtime and costly repairs.
6. Condition monitoring
Condition monitoring is the process of monitoring the condition of assets and equipment to identify potential problems before they cause major disruptions to operations. It is an important component of maintenance and logistics tracking, as it can help to identify and address potential problems before they cause major disruptions to operations.
- Data collection
The first step in condition monitoring is to collect data from assets and equipment. This data can include information such as temperature, vibration, and power consumption. Data can be collected using sensors that are attached to the assets and equipment.
- Data analysis
Once data has been collected, it must be analyzed to identify patterns and trends. This can be done using a variety of statistical techniques. Data analysis can be used to identify assets and equipment that are at risk of failure and to predict when that failure is likely to occur.
- Scheduling maintenance
Once assets and equipment have been identified as being at risk of failure, maintenance can be scheduled to address the issue before the asset or equipment fails. This can help to prevent unplanned downtime and costly repairs.
- Benefits of condition monitoring
Condition monitoring can provide a number of benefits, including:
- Reduced downtime
- Improved equipment reliability
- Lower maintenance costs
- Increased productivity
Condition monitoring is a powerful tool that can help organizations to improve their maintenance and logistics operations. By using data and analytics to monitor the condition of assets and equipment, organizations can identify and address potential problems before they cause major disruptions to operations.
7. Fleet management
Fleet management is the process of managing a fleet of vehicles, including planning, organizing, and controlling the use of vehicles and drivers. It is an important component of maintenance and logistics tracking, as it helps to ensure that vehicles are properly maintained and utilized, and that goods and materials are delivered on time and in good condition.
- Vehicle maintenance
Fleet management involves tracking the maintenance history of vehicles, scheduling maintenance appointments, and ensuring that vehicles are properly maintained. This helps to prevent breakdowns and failures, and to extend the lifespan of vehicles.
- Vehicle tracking
Fleet management systems can be used to track the location of vehicles in real time. This information can be used to optimize routing, improve customer service, and respond to emergencies.
- Driver management
Fleet management involves managing drivers, including hiring, training, and scheduling. Fleet managers also need to ensure that drivers are properly licensed and insured, and that they comply with all applicable laws and regulations.
- Fuel management
Fleet management involves managing fuel consumption, including tracking fuel usage, negotiating fuel contracts, and implementing fuel-saving strategies. This helps to reduce fuel costs and improve the efficiency of fleet operations.
Effective fleet management can help to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of maintenance and logistics operations. It can also help to reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
8. Supply chain management
Supply chain management (SCM) is the process of planning, organizing, and controlling the flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers. It involves coordinating and managing all the activities involved in producing and delivering a product or service, from the sourcing of raw materials to the delivery of the finished product to the customer.
Maintenance and logistics tracking is an important component of SCM. It helps to ensure that the right products are delivered to the right place, at the right time, and in the right condition. Maintenance and logistics tracking can also help to identify and resolve problems in the supply chain, such as delays, shortages, and quality issues.
For example, a manufacturer might use maintenance and logistics tracking to track the movement of raw materials from suppliers to the factory, and then to track the movement of finished goods from the factory to customers. This information can be used to identify any delays or problems in the supply chain, and to take corrective action to prevent them from impacting the delivery of products to customers.
Effective maintenance and logistics tracking can help organizations to improve their supply chain efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. By understanding the connection between supply chain management and maintenance and logistics tracking, organizations can develop and implement strategies to improve the overall performance of their supply chains.
9. Data analytics
Data analytics plays a crucial role in maintenance and logistics tracking by providing valuable insights and patterns that can help organizations optimize their operations, reduce costs, and improve efficiency. Through the analysis of vast amounts of data, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of their maintenance and logistics processes, enabling them to make data-driven decisions that lead to improved outcomes.
- Predictive maintenance
Data analytics can be used to predict when equipment is likely to fail, allowing organizations to schedule maintenance proactively before breakdowns occur. This can help to prevent unplanned downtime, reduce maintenance costs, and improve equipment lifespan.
- Inventory optimization
Data analytics can be used to optimize inventory levels, ensuring that organizations have the right amount of inventory on hand to meet demand without overstocking. This can help to reduce inventory carrying costs, improve cash flow, and free up space for other purposes.
- Route optimization
Data analytics can be used to optimize delivery routes, taking into account factors such as traffic patterns, weather conditions, and customer locations. This can help to reduce delivery times, improve customer satisfaction, and lower transportation costs.
- Performance monitoring
Data analytics can be used to monitor the performance of maintenance and logistics activities, identifying areas for improvement. This can help to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure that maintenance and logistics operations are aligned with organizational goals.
Overall, data analytics is a powerful tool that can help organizations to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their maintenance and logistics operations. By leveraging data to gain insights and make informed decisions, organizations can optimize their processes, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
FAQs on Maintenance and Logistics Tracking
Maintenance and logistics tracking is a critical aspect of any organization’s operations, helping to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about maintenance and logistics tracking:
Question 1: What are the benefits of maintenance and logistics tracking?
Answer: Effective maintenance and logistics tracking can provide numerous benefits, including improved asset utilization, reduced maintenance costs, enhanced customer satisfaction, and improved regulatory compliance.
Question 2: How can organizations implement maintenance and logistics tracking?
Answer: Maintenance and logistics tracking can be implemented through manual methods, such as spreadsheets and databases, or through specialized software solutions. Automated tracking systems offer greater efficiency and accuracy.
Question 3: What are some key components of maintenance and logistics tracking?
Answer: Key components of maintenance and logistics tracking include asset management, inventory control, work order management, preventive maintenance, predictive maintenance, condition monitoring, fleet management, supply chain management, and data analytics.
Question 4: How does data analytics contribute to maintenance and logistics tracking?
Answer: Data analytics plays a crucial role in maintenance and logistics tracking. It enables organizations to analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict failures, optimize inventory levels, and improve overall performance.
Question 5: What are some best practices for maintenance and logistics tracking?
Answer: Best practices for maintenance and logistics tracking include establishing clear goals, selecting the right technology, implementing standardized processes, training staff effectively, and continuously monitoring and evaluating performance.
Question 6: How can organizations ensure the accuracy and reliability of maintenance and logistics tracking data?
Answer: Organizations can ensure data accuracy and reliability by using reliable data sources, implementing data validation processes, and conducting regular audits to verify the integrity of the data.
By addressing these common questions, organizations can gain a better understanding of maintenance and logistics tracking, its benefits, and how to implement it effectively. This can help them optimize their maintenance and logistics operations, leading to improved efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Transition to the next article section:
Maintenance and Logistics Tracking Tips
Effective maintenance and logistics tracking is essential for optimizing operations, reducing costs, and improving customer satisfaction. Here are some valuable tips to enhance your maintenance and logistics tracking practices:
Tip 1: Establish Clear Goals
- Define the specific objectives of your maintenance and logistics tracking system.
- Determine the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will measure the effectiveness of your system.
Tip 2: Select the Right Technology
- Evaluate different maintenance and logistics tracking software solutions to find the one that best meets your needs.
- Consider factors such as functionality, ease of use, scalability, and integration capabilities.
Tip 3: Implement Standardized Processes
- Develop clear and consistent processes for data collection, analysis, and reporting.
- Use standardized templates and checklists to ensure data accuracy and completeness.
Tip 4: Train Staff Effectively
- Provide comprehensive training to all personnel involved in maintenance and logistics tracking.
- Ensure that staff members understand the importance of accurate data entry and interpretation.
Tip 5: Continuously Monitor and Evaluate Performance
- Regularly review the performance of your maintenance and logistics tracking system.
- Identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments to optimize the system’s effectiveness.
Tip 6: Ensure Data Accuracy and Reliability
- Use reliable data sources and implement data validation processes to ensure the accuracy of your data.
- Conduct regular audits to verify the integrity and completeness of your data.
Tip 7: Leverage Data Analytics
- Use data analytics tools to analyze maintenance and logistics data to identify trends and patterns.
- Gain insights that can help you optimize maintenance schedules, improve inventory management, and enhance supply chain efficiency.
Tip 8: Foster Collaboration and Communication
- Encourage collaboration between maintenance, logistics, and other departments to ensure a holistic approach to tracking.
- Establish clear communication channels to facilitate the sharing of information and best practices.
By following these tips, organizations can establish a robust and effective maintenance and logistics tracking system that drives operational excellence, reduces costs, and improves customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Maintenance and logistics tracking is a crucial aspect of modern business operations, enabling organizations to optimize their assets, streamline their supply chains, and enhance customer satisfaction. By implementing effective maintenance and logistics tracking systems, organizations can gain visibility and control over their operations, leading to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and increased profitability.
The exploration of maintenance and logistics tracking in this article has highlighted the key components, benefits, and best practices associated with this essential discipline. Organizations that embrace maintenance and logistics tracking can gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic business environment, where efficiency and customer-centricity are paramount.